Health - Socially Healthy Relationships
(middle grades)
Activity and Lesson plan
- Overview
- Big ideas, concepts, facts, & outcomes
- Communication & relationship concepts & outcomes
- Decision making concepts, facts, & outcomes
- Pedagogical overview
- Unit lesson plan activity sequence
- Resources and materials
- Scoring guide suggestions
- Lesson plans
- Healthy relationships
- Respect yourself
- Communicate well
- Family relationships
- Peer relationships
- Ideal group members
- Peer relationships in problem solving groups
- Assertive survey
- Procedure, script, and role play
- Crossword puzzles
- Lab Notes for activities
- Brainstorm healthy relationships and Healthy relationships
- Respect yourself
- Communicate well
- Family relationships
- Peer Relationships
- Ideal group members
- Interactions in cooperative groups
- Assertive survey, behaviors, refusal skills and role play
- Role play social skill
- Crossword puzzles
- Fact Sheets
- Healthy relationships
- Respect yourself & others
- Communicate well
- Family relationships
- Peer relationships
- Listening
- Stand up for your rights
- Assertive behavior procedure
- Making health decisions
- Word bank
- References
Overview
A plan to review and develop a person's ability to foster healthy relationships. Relationships can be beneficial and detrimental to our mental, emotional, social, and physical health. They affect the quality of the decisions people make, which can impact their health and wellness.
This unit includes activities for students to develop a plan to maintain and improve their mental and emotional health. It reviews mental / emotional health and beneficial and detrimental behaviors that affects health and influences the decisions people make that promote or risk health and wellness. Decisions often made without sufficient critical thought.
Activities include: investigating relationships, self-respect, communications, family relationships, peer relationships, cooperation, and assertiveness.
Background information:
This plan is designed for students who have prior knowledge in the dimensions of health, decision making, mental and emotional health. This plan is designed as an investigation for middle level students in social health and relationships. However, no background information, other than being middle level age, is necessary.
Additional study topics included in this middle school curriculum:
Big ideas, concepts, facts, and outcomes
Health standards
Big ideas and specific outcomes:
- Standard 1 - Students will comprehend concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention to enhance health.
- Standard 2 - Students will analyze the influence of family, peers, culture, media, technology, and other factors on health behaviors.
- Standard 3 - Students will demonstrate the ability to access valid information and products and services to enhance health.
- Standard 4 - Students will demonstrate the ability to use interpersonal communication skills to enhance health and avoid or reduce health risks.
- Standard 5 - Students will demonstrate the ability to use decision-making skills to enhance health.
- Standard 6 - Students will demonstrate the ability to use goal-setting skills to enhance health.
- Standard 7 - Students will demonstrate the ability to practice health-enhancing behaviors and avoid or reduce risks.
- Standard 8 - Students will demonstrate the ability to advocate for personal, family, and community health.
Related concepts and facts
Big idea: Everyones health and wellness is dependent on relationships. Relationships with family, peers, and others provide what is necessary to maintain physical, mental, and social health. Relationships that work to provide and advocate for personal, family, and community health and wellness, improved with reasoned decision making, effective interpersonal communication skills, and advocacy for each other.
- Better decisions are made when relationships are considered.
- Relationships improve with practice.
- Relationships improve when a person respects them self, communicates well, has good social skills, knows skills useful to cooperation and collaboration when appropriate and when to resolve conflict or refuse and move on.
Outcome
Demonstrate skill relating to others by knowing how to interact socially to build relationships, resolve conflicts, or other actions to maintain personal and community health and wellness.
Communication, Relationships as health enhancing behaviors, & advocacy
Specific Standards
Communication
4.12.1 Utilize skills for communicating effectively with family, peers, and others to enhance health.
4.12.2 Demonstrate refusal, negotiation, and collaboration skills to enhance health and avoid or reduce health risks.
4.12.3 Demonstrate strategies to prevent, manage, or resolve interpersonal conflicts without harming self or others.
4.12.4 Demonstrate how to ask for and offer assistance to enhance the health of self and others.
Enhance health
7.12.1 Analyze the role of individual responsibility for enhancing health.
7.12.2 Demonstrate a variety of healthy practices and behaviors that will maintain or improve the health of self and others.
Advocate
8.12.1 Utilize accurate peer and societal norms to formulate a health-enhancing message.
8.12.2 Demonstrate how to influence and support others to make positive health choices.
8.12.3 Work cooperatively as an advocate for improving personal, family, and community health.
8.12.4 Adapt health messages and communication techniques to a specific target audience.
Big ideas:
- Communication skills are necessary to enhance health and avoid or reduce health risks. (4 communicate)
- Good relationships are necessary to implement health enhancing behaviors and avoid or reduce risks. (7 enhance)
- Community health is dependent on our advocacy for each other. (8 advocate)
Related concepts and facts
Communication (4)
- Communication is enhanced with practice.
- Communication is necessary to learn healthy practices.
- Communication is necessary for healthy relationships.
Enhance health (7)
- Relationships with family, peers, and others provide what is necessary to maintain and enhance physical, mental, and social health.
- Better health decisions are made when relationships are considered.
- Health enhancing behaviors are improved with greater ability to interact socially, to build relationships, resolve conflicts, and other social actions.
- Relationships improve with practice.
- Relationships improve when a person respects them self, communicates well, has good social skills, knows skills useful to cooperate and collaborate as appropriate and when to resolve conflict or refuse and move on.
- Relationships are enhanced with the exchange of useful information, caring relationships, helpful actions, and provision of needs.
Advocate (8)
- Everyones health and wellness is dependent on advocacy.
- Relationships that work to provide and advocate for personal, family, and community health and wellness, improve with reasoned decision making, effective interpersonal communication skills, and advocacy for each other.
Outcomes
- Demonstrate the ability to use interpersonal communication skills to enhance health and avoid or reduce health risks. (4)
- Demonstrate the ability to practice health-enhancing social relationship behaviors to improve health and wellness and avoid or reduce risks. (7)
- Demonstrate the ability to advocate for personal, family, and community for health and wellness. (8)
Decision-making skills to enhance health.
Big ideas: It is important to know how to discover accurate verifiable information about different _ to make good healthy decisions. Decision-making skills are necessary to identify, implement, and sustain health-enhancing behaviors. This includes essential steps needed to make healthy decisions applied to health, safety, and social issues to enable people to individually or in collaboration with others improve people's quality of life.
Related concepts and facts
- Health and safety problems are related to decision making.
- The better a person knows them self, the better decisions they will make.
- Effective social skills improve communication and getting along with people.
- Thinking about a problem before experiencing it helps make better decisions.
- There are positive and negative consequences for all decisions.
- There are positive and negative influences to consider when making decisions.
Outcome
- Describe the relationships between making good decisions and being healthy.
- Describe a decision making process that includes identification of a problem, alternative solutions with positive and negative consequences, and implementation suggestions.
- Describe positive and negative influences that impact decision making.
- Use a decision making process to make safe and healthy decisions that improve people's quality of life.
Specific outcomes -
2.12.1 Analyze how family influences the health of individuals.
2.12.2 Analyze how culture supports and challenges health beliefs, practices, and behaviors.
2.12.3 Analyze how peers influence healthy and unhealthy behaviors.
2.12.4 Evaluate how the school and community can impact personal health practice and behaviors.
2.12.5 Evaluate the effect of media on personal and family health.
2.12.6 Evaluate the impact of technology on personal, family, and community health.
2.12.7 Analyze how the perceptions of norms influence healthy and unhealthy behaviors.
2.12.8 Analyze the influence of personal values and beliefs on individual health practices and behaviors.
2.12.9 Analyze how some health risk behaviors can influence the likelihood of engaging in unhealthy behaviors.
2.12.10 Analyze how public health policies and government regulations can influence health promotion and disease prevention
3.12.1 Evaluate the validity of health information, products, and services.
3.12.2 Utilize resources from home, school, and community that provide valid health information.
3.12.3 Determine the accessibility of products and services that enhance health.
3.12.4 Determine when professional health services may be required.
3.12.5 Access valid and reliable health products and services.
4.12.1 Utilize skills for communicating effectively with family, peers, and others to enhance health.
4.12.2 Demonstrate refusal, negotiation, and collaboration skills to enhance health and avoid or reduce health risks.
4.12.3 Demonstrate strategies to prevent, manage, or resolve interpersonal conflicts without harming self or others.
4.12.4 Demonstrate how to ask for and offer assistance to enhance the health of self and others.
5.12.1 Examine barriers that can hinder healthy decision making.
5.12.2 Determine the value of applying a thoughtful decision-making process in health-related situations.
5.12.3 Justify when individual or collaborative decision making is appropriate.
5.12.4 Generate alternatives to health-related issues or problems.
5.12.5 Predict the potential short and long term impact of each alternative on self and others.
5.12.6 Defend the healthy choice when making decisions.
5.12.7 Evaluate the effectiveness of health related decisions.
Pedagogical Overview
Activity Lesson Plan Sequence to provide sufficient opportunities for students to achieve the targeted outcomes.
Make sure students have the prior knowledge identified in the background information.
- Activity 1 - Health relationships - Students Brainstorm from their prior knowledge about . Focus student's attention by asking the overall focus question, then ask and discuss the sub focus questions and set learning goals.
- Activity 2 - Respect yourself and others
- Activity 3 - Communicating well
- Activity 4 - Family relationships
- Activity 5 - Peer relationships
- Activity 6 - Ideal group members
- Activity 7 - Peer relationships in problem solving groups
- Activity 8 - Assertive behaviors, refusal skills, and role play
- Activity 9 - Social skill role play. Use a social skill procedure to write a script and role play listening & standing up for your rights
- Crossword puzzles
- Review
- Review with answer key
Focus question
Unit focus question:
What kinds of decisions do people make when they interact with other people?
Sub focus questions:
- What makes a healthy relationship?
- How do people nurture healthy relationships?
Resources and Materials
- Activity 1 - Brainstorming healthy relationships and Healthy relationships
- Activity 2 - Respecting yourself
- Activity 3 - Communicating well
- Activity 4 - Family relationships
- Activity 5 - Peer Relationships
- Activity 6 - Ideal group members
- Activity 7 - Peer relationships in problem solving groups
- Activity 8 - Assertive survey, behaviors, refusal skills and role play
- Activity 9 - Social skill role play. Use a social skill procedures to write a script and role play a social situation. (listening & assertive)
- Crossword puzzles: 1. Warm-up, 2. Expert, 3. Comprehensive
- Healthy relationships
- Respect yourself --- see also ways to increase self-esteem...
- Communicating well
- Relationship crossword puzzle May do here or anytime till end (external file)
- Family relationships
- Peer relationships
- Listening
- Standing up for your rights
- Assertive behavior and refusal procedure
References and additional resources
Scoring guides suggestions (rubric)
Decision making skills to enhance health (scoring guide)
Top level
- Top level: Makes decisions with a process that includes focus on a process, accurate information, identification of a problem, analysis, generation of alternative options and choices with positive and negative consequences, implementation, and evaluation suggestions. And describes benefits of a comprehensive decision making process.
- Upper level: Makes decisions with a process that includes identification of a problem, alternative solutions with positive and negative consequences, and implementation suggestions. And describes benefits of a comprehensive decision making process.
- Middle level: Makes decisions with a multiple step process that uses several appropriate steps for making decisions and excludes some that may be necessary to make better decisions.
- Low level: Makes decisions subconsciously and emotionally or in a manner that believes will result in the best rewards personally or socially (parents, teachers, friends, ...).
Lower level
Social interactions in a conflict situation (scoring guide)
Top level
- Upper level: Social interactions recognize a conflict between subconscious influences and logical consequences and identify multiple ways to resolve conflict with respect to accept each person's individual rights of assertion, and use appropriate social skills when focusing on and stating the problem, analyzing the problem, stating alternative options and choices with positive and negative consequences, and communicating decisions that most individuals accept.
- Middle level: Social interactions seem to recognize a conflict between subconscious influences and logical consequences while recognizing different ways to resolve conflict and attempt to solve problems with regard to individual rights of assertion and use of applicable social skills to make or accept a decision that most individuals can accept.
- Low level: Social interactions seem to be driven by subconscious emotional influences in a manner that suggests decisions are based on influences for immediate personal or social outcomes and rewards, without regard to individual rights, concern for conflict resolution, or use of applicable social skills.
Lower level
Scenario Activity Rubric with outcomes & scoring guide
Advocacy related outcomes ( 5 points) Total ______ / 100
- Presented and advocated positive health choices.
- Presented and promoted information that was health-enhancing.
- Interacted with awareness of the audience.
- Encouraged others to make healthy choices.
- Demonstrated passion or conviction for the information presented.
Goal Setting related outcomes ( 5 points)
- Focused on the presentation as the goal.
- Created a work path that was realistic and attainable.
- Selected an effective strategy and plan to implement and achieve the goal.
- Monitored, evaluated, and reflected on the plan and its implementation and made adjustments as necessary.
Communication related outcomes ( 50 points)
Presentation completed __ Data sheet completed __ Review completed __
- Clear - idea or group of ideas are easy to understand.
- Precise - accurate and exact explanation of the idea or ideas with appropriate and sufficient detail.
- Reliable - consistently good quality and able to be trusted.
- Logical - ideas fit together without discrepancies and sufficiently support the conclusions.
- Relevant - idea or ideas fit the purpose.
- Consistent - idea or ideas are supported by observation, current research, or wisdom of practice. Novel ideas are developed with plausible explanations.
- Comprehensive - contains necessary and sufficient big ideas and supporting information to communicate the idea or group of ideas with complexity and connectedness with multiple perspectives.
- Unbiased - fair nonprejudicial presentation of information.
Group interactions
- Interactions with group members assisted achievement of appropriate goals.
- Used appropriate listening skills.
- Distinguished between supported factual information and beliefs or emotional feelings by stating "I think" or "I feel" or using I statements.
- Used a respectful tone.
- Used appropriate body language.
- Supported their messages with research, logical reasoning, and meaningful explanations.
Decision Making related outcomes (10 points)
Decisions for planning and presenting their presentation
- Top level: Makes decisions with a process that includes focus on a process, accurate information, identification of a problem, analysis, generation of alternative options and choices with positive and negative consequences, implementation, and evaluation suggestions. And describes benefits of a comprehensive decision making process. (10)
- Upper level: Makes decisions with a process that includes identification of a problem, alternative solutions with positive and negative consequences, and implementation suggestions. And describes benefits of a comprehensive decision making process. (9)
- Middle level: Makes decisions with a multiple step process that uses several appropriate steps for making decisions and excludes some that may be necessary to make better decisions. (8)
- Low level: Makes decisions subconsciously and emotionally or in a manner that believes will result in the best rewards personally or socially (parents, teachers, friends, ...). (7)
Analyzing Influences related outcomes ( 5 points)
- Identified and analyzed personal influences and how they vary.
- Identified social biases and influences that affected accuracy of information and decision making.
- Interpreted how conditions and influences impact relationships and used this information to better make decisions, set goals, communicate, advocate for health, and achieve goals.
Accessing Information related outcomes ( 5 points)
Took steps to get valid health information and appropriate health services.
- Cited sources.
- Evaluated the validity of sources.
- Mentioned appropriate health resources for the problem.
- Included specific types of help available for different needs.
Refusal Skills related outcomes ( 5 points)
- Included the word "no" in any refusal response.
- Provided an explanation of why in any refusal response.
- Offered appropriate alternatives in place of the proposed activity that is being rejected.
- Used body language that supported the communication of refusal.
- Included a description of "moving on" from the situation.
Self-Management Skills related outcomes ( 5 points)
- Included healthy behaviors and habits for a person to affect relationships in a healthy way.
- Identified social behaviors and procedures to achieve a healthy relationships.
- Described and demonstrated a procedure for healthy relationships (.......................)
Conflict Resolution related outcomes ( 5 points)
- Identified problems if they occurred
- Invented options for the group's benefit
- Agreed on a solution that benefited the group
- Interactions to solve conflicts were:
- Upper level: Social interactions recognize a conflict between subconscious influences and logical consequences and identify multiple ways to resolve conflict with respect to accept each person's individual rights of assertion and use appropriate social skills when focusing on and stating the problem, analyzing the problem, stating alternative options and choices with positive and negative consequences, and communicating decisions that most individuals accept. (5)
- Middle level: Social interactions seem to recognize a conflict between subconscious influences and logical consequences while recognizing different ways to resolve conflict and attempt to solve problems with regard to individual rights of assertion and use of applicable social skills to make or accept a decision that most individuals can accept. (4)
- Low level: Social interactions seem to be driven by subconscious emotional influences in a manner that suggests decisions are based on influences for immediate personal or social outcomes and rewards, without regard to individual rights, concern for conflict resolution, or use of applicable social skills. (3)
Stress Management related outcomes ( 5 points)
- Identified situations that caused stress
- Demonstrated techniques to manage and reduce stress (talking about it, relaxation strategies, getting to work, not procrastinating ...)
This scoring guide is based on the Healthy Practices Skills and Outcomes for a middle level health course, which are heavily influenced by the national health standards.
Lesson Plans
Activity 1 - Healthy relationships
Materials:
- Brainstorming guidelines
- Brainstorming healthy relationships - lab notes
- Healthy relationships - lab notes
- Ideas for healthy relationship - fact sheet
Focus questions:
- What are relationships?
- What makes a healthy relationship?
- How do people nurture healthy relationships?
Learning outcomes:
- Define healthy relationships as having respect for yourself, respect for others, able to trust others, set goals, make decisions, know how to care for your self and others, have good family relationships, good peer relationships, know how to communicate ideas and emotions, develop good social skills, cooperate, and resolve conflicts.
Suggested procedures overview:
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and assess their initial understanding of the focus questions.
- Give students the fact sheet, share ideas, discuss
- Complete lab notes four parts.
Exploration
- Put students in groups.
- Provide Brainstorming healthy relationships - lab notes
- Brainstorm answers to.
- What are relationships? Relationship is the manner in which people are connected. Relationships will vary according to who you interact with and where the interactions take place: home - family, school - peers, teachers, counselors... community - friends, customer representatives, sales people, strangers, and the purpose of the relationships.
- What makes a healthy relationship?
- Relationships are enhanced with the exchange of useful information, caring relationships, helpful actions, and provision of needs.
- Information necessary to maintain and enhance physical, mental, and social health.
- When a person respects them self, communicates well, has good social skills, knows skills useful to cooperate and collaborate as appropriate and when to resolve conflict or refuse and move on.
- How do people nurture healthy relationships?
- Have groups share their ideas and move to invention.
Invention
- Review relationship in word bank - Relationship is the manner in which people are connected. Relationships will vary according to who you interact with and where the interactions take place: home - family, school - peers, teachers, counselors... community - friends, customer representatives, sales people, strangers, ...
- Provide the lab notes Healthy relationships
- Tell. Categorize the 16 actions.
- Provide the fact sheet with ideas for healthy relationships
- Tell. Students to look over the list of ideas.
- Ask To explain how some ideas on the list relate to health.
- Tell. On your lab notes, Write goals to describe characteristics you use or would like to use for healthy relationships.
- Tell. On your lab notes write how relationships affect the three areas of health.
Activity 2 - Respect yourself and others
Materials:
- Review the article Motivational Theory and Self-Efficacy to prepare for this activity (Respecting yourself and others). Review the attributes that affect self-esteem and self-efficacy, how the flow chart explains self-efficacy and success, and research for examples and suggestion.
- Respecting yourself & others - Lab notes
- Respecting yourself and others - fact sheet
- Stand up for your rights - fact sheet
- Assertive behavior and refusal skill - fact sheet in mental emotional behavior.
- Body image, media resources -
- 1st Dove evolution video - Original video of behind the scenes of image manipulation that spreads unattainable standards of beauty. (1:16)
- Image sketches - explores how we perceive ourselves & other people perceive us. (3:00 mins)
- Image sketches from mother's and daughter's perspectives. (2:58 mins)
- Body image evolution time lapse video of photo shopping of a model's body. (1:11mins)
Focus questions:
- What do people do that demonstrate a respect for them self and others?
Learning outcomes:
-
Describe characteristics of respecting yourself and others.
Suggested procedures overview:
- Discuss what people do that demonstrates respect for them self and others.
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and assess their initial understanding of the focus questions.
- Students review fact sheets and write a goal for each of seven categories.
Scoring guide for
Top level
- Include a comprehensive list of goals that include a positive goal in categories: 1. needs, 2. self esteem & self-efficacy, 3. respect for self, others, and the environment, 4. family and peer relationships, 5. able to communicate, 6. be assertive, and 7. social skills.
Lower level
Exploration
- Put students in pairs or small groups of three or four.
- Provide students with Respecting yourself and others Lab notes.
- Tell. People who respect themselves and others generally have better health. Therefore, it would be good to explore what people do that suggests they respect themselves and others.
- Ask and discuss:
- What do people do that shows respect for themselves and others? Accept all answers to review what students know.
- Take care of themselves.
- Meet their needs and others.
- Be nice to yourself.
- Be nice to other people.
- Care for others.
- Set good goals and achieve them.
- Learn and use social skills.
- Learn how to be assertive and when it is appropriate to be assertive.
- Don't waste stuff, reuse, recycle.
- Learn to improve self, our tools, and what we make.
- Develop a set of rules and codes to live by that are ethical.
- Use the ideas students identified & form categories:
- Able to meet your needs and others (Maslow)
- Understand and have good self-esteem & self-efficacy
- Respect self, others, & environment
- Family and peer relationships
- Able to communicate
- Be assertive
- Social skills
- Tell. In the coming activities we are going to review each of these and develop goals for each in this activity and in later activities develop procedures to get better doing them.
- Tell. We will review ideas for each of these with the fact sheet and then write a goal for each of the seven.
Invention
- Let's go.
- First, We have reviewed the importance of having needs met with Maslow's Hierarchy so you can use them to write that goal later.
- Next, is self-esteem and self-efficacy. Let's start with a video for these.
- Share the 1st Dove evolution video - Original video of behind the scenes of image manipulation that spreads unattainable standards of beauty. (1:16)
- Discuss how media manipulates the ways a person might respect themselves and affects self-esteem. Media provides unrealistic standards to compare ourselves with and may cause us to set unrealistic goals or to give up on setting goals, because we see them as unattainable. Which is true compared to photo shopped images. Lack of success leads to low self-esteem.
- Tell. Good relationships start with respect for yourself and how you feel about yourself and how you meet your needs and the needs of others.
- Tell. One way to feel good about yourself is to be successful. Success increases self-esteem. And the more people believe they can be successful, then the greater their self-efficacy.
- Provide students with the Respecting yourself and others fact sheet
- Ask. What is self-esteem & self-efficacy? Definitions on Respecting yourself and others Lab note.
- Self-esteem is the value, respect, and confidence you have for yourself.
- Self-efficacy is the belief or understanding a person has in their ability to succeed in specific situations or accomplish a task.
- Continue with the Respecting yourself and others fact sheet and the second category or self-esteem and self-efficacy focusing on Attributes that contribute to the perception of success or failure and affect self-esteem.
- Ask. What variables on the chart affect success and failure? Ability, effort, task, & luck
- Ask. What does it mean for variables to be stable or unstable. That they can change or not. Like ability can be changed, effort can be changed, the task can be changed, and luck can change. Or believe that one or more don't change. A person's ability is set and effort doesn't matter.
- Ask. What does it mean for variables to be internally controlled or externally controlled. Internally controlled means each person controls their ability, effort, task, and luck. Externally means someone or something else has control of it being changed.
- Ask. Explain the flow chart. It suggests that when a person sets a goal, selects a strategy, and is successful they mostly believe they were so, because of their effort, ability, and strategy. If they are not successful they often believe it was because of inability, lack of effort, unlucky, poor strategy or difficult task.
- Ask. How do beliefs about the variables affect the way people act? If they believe they have the power (internal control) to change and it is possible to change (unstable- changeable), then they will more likely adjust and try again until they are successful.
- Ask. What does all this mean for self-esteem or self-efficacy? Success breeds success. Success makes us feel good about ourselves, Success makes us believe we will be successful in the future.
- Continue with number three. Respect self, others, and relationships.
Suggest they get ideas for this goal for their personal identity from the activity Who am I? Personal Shield or Coat of Arms. If they are wanting more traits, they could consider: trustworthy, loyal, helpful, friendly, courteous, kind, cheerful, caring, fair, responsible, respectful, a good citizen, or others. - Four. Ask them to think about a goals related to good relationships and mention they will review and use these ideas for better Family and Peer in activities later.
- Five. Ask them to think about a goals related to communicate well and mention they will review and use these ideas to Communicate well in activities later..
- Six. Ask them to think about goals related to standing up for your rights and being assertive and mention they will review and use these ideas in activities later.
- Seven. Ask them to think about a goals related to social skills for respectful interactions and mention they will review and use social skills and their procedures in later activities.
Discovery
- Tell. Write personal goals you use or would like to use to respect yourself and others in each of the categories we created.
- Needs (Maslow)
- I will consider my needs and others to make respectful decisions.
- Understand and have good self-esteem & self-efficacy
- I will seriously reflect on my successes and failures to accurately decide if I should accept the outcome or take more personal charge to control effort, strategy, task, or ability to achieve success.
- Respect self, others, & environment
- I will review my Coat of Arms and define me in ways I see as respectful.
- Relationships
- I will work to maintain and improve respectful relationships with peers and family.
- Communicate
- I will study what makes for better communication and work to be a respectful communicator.
- Be assertive
- I will review procedure (suggestions) for being assertive and use them in appropriate situations.
- Social skills.
- I will study social skills and work to help people set and achieve goals that benefit us and the environment.
- Needs (Maslow)
Activity 3 - Communicate well
Materials:
- Communicate well - Lab notes
- Communicate well - Fact sheet
- Social skills How to teach and learn them, procedures, charts of what they look, sound, feel like.
Focus questions:
- How do we communicate well?
Learning outcomes:
- Identify guidelines for good communication: Be open, courteous and respectful, use appropriate body language, listen, use wait time, be thoughtful and open minded - don't jump to conclusions, use clear concise language, if you have a purpose, make it clear, know your audience, define terms, repeat what you think you understand, check for understanding, ask questions,
Suggested procedures overview:
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and assess their initial understanding of the focus question - How do we communicate well.
- Discuss.
- Have students review the communication fact sheet and have them write their guidelines to communicate well.
Exploration
- Put students in pairs or groups of three or four.
- Distribute the Communicate Well - lab notes
- Ask. How do we communicate well? Accept all reasonable answers.
Invention
- Tell. To communicate well people use general guidelines and develop specific procedures for certain social situations. First, we will construct some guidelines and then later activities groups will select a social skill to investigate, create a procedure and demonstrate to the class.
- Distribute the Communicate well - fact sheet
- Tell. Review the fact sheet and write guide lines for communicating well.
- Have groups share their guide lines.
- Combine groups ideas and create a class list of guidelines for communicating well.
Activity 4 - Family relationships
Materials:
Focus questions:
- How do family relationships affect health and wellness?
Learning outcomes:
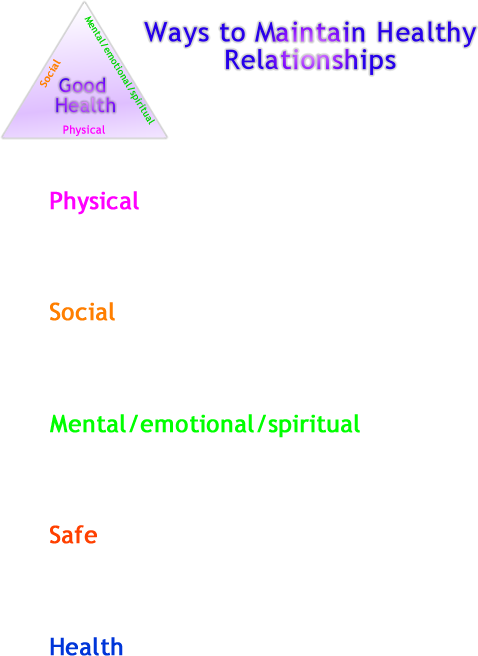
- Describe relationships that maintain physical, social, and mental/ emotional safe and healthy family.
- Sort family actions into categories that affect health and wellness: physical, social, mental/emotional/spiritual, safe, health
Suggested procedures overview:
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and assess their initial understanding of the focus questions.
- Have students create guidelines for strong family relationships.
Exploration
- Put students in pairs or groups of three or four.
- Distribute. Family relationships - lab notes
- Ask. How do family relationships affect health and wellness? Accept all reasonable answers.
- Parents introduce their children to different kinds of food, nutrition, physical activities, sports, inside & outside activities, recreation, mental activities, reading, music, dance, travel, friends, immediate family and extended family, home, sleeping & resting spaces, eating meals together at home restaurant or fast food to go, ...
Invention
- Distribute the fact sheet Family relationships
- Tell. Sort the family actions that affect health and wellness on, on the fact sheet, into the five categories on the lab notes: physical, social, mental/emotional/spiritual, safe, health
- Share results.
- physical - provide physical needs, introduce and encourage activity or inactivity. Indoor or outdoor, sports, couch potato, different kinds of activity aerobic, weight training,
- Social - teach respect for self & others, teach how to work together, first introduce you to friends, family, neighbors ... later approve and encourage or discourage social interactions. Teach social skills directly or by modeling appropriate or inappropriate behaviors, teach and model cooperation and working with others,
- Mental/emotional/spiritual - teach values & morals, teach and model appropriate and inappropriate ways to handle problems, handle stress, what to learn and spend time on (art, music, reading, TV, video, sports, outdoor recreation, swimming, camping, electronic devices, ...)
- Safety - Young children, child proof home, put chemicals out of reach, use gun locks and safes, use cabinet locks to store poisonous chemicals and other harmful items, require everyone to wear seat belts in vehicles, bike helmets, model and teach where to get help: counseling services, support groups, crisis center, community shelters, hot lines, law enforcement, hospitals, clinics, rescue units, fire, and how to take action against abuse with 3R's: recognize, resist, and report.
- Health - Provide regular check ups, provide vaccinations as recommended, dental appointments, skin care, vision care, provide healthy food, exercise, teach stress management, relaxation techniques, encourage learning, creativity, music, art ...
Activity 5 - Peer relationships
Materials:
Focus questions:
- What do people do that encourage peer relationships or discourage peer relationships?
Learning outcomes:
- List actions that encourage peer relationships and discourage peer relationships.
Suggested procedures overview:
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and assess their initial understanding of the focus questions.
- Ask. What do people do that encourage peer relationships or discourage peer relationships?
- Have students categorize actions as positive, negative, or neutral effects on peer relationships.
- Discuss.
Exploration
- Put students in pairs or groups of three or four.
- Distribute the Lab note.
- Ask. What do people do that encourage peer relationships or discourage peer relationships?
- Tell. List two or three actions or behaviors on the lab notes for encourage and discourage peer relationships.
- Encourage - listen, smile, offer help as appropriate, encourage appropriate behavior, ...
- Discourage - interrupt, push your own agenda, make fun of some members, laugh at mistakes, ...
- Discuss
- Tell. Let's look at some behaviors, on your lab note, and classify them as positive, negative, or neutral for relationship building.
- Review and discuss.
Invention
- Review information on the key ideas for peer relationship fact sheet , identify behaviors that build relationships, describe what a person should consider when considering expanding a relationship, describe how to maintain friendships when a friend chooses activities with others.
- Discuss.
- Introduce next activity as an opportunity to look at relationships for group members.
Activity 6 - Ideal group members
Materials:
Focus questions:
- What are the traits you want your group members to have?
Learning outcomes:
- Identify traits that assist groups in being successful.
Suggested procedures overview:
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and assess their initial understanding of the focus questions.
- Tell students they are going to pick one of two types of apps that selects members for your group.
Exploration
- Put students in pairs or groups of three or four.
- Distribute the group relationships lab notes
- Tell. You are going to pick one of two types of apps that selects members for your group.
- App 1 selects group members, for a class project, according to the traits you believe a good group member should have.
+ have the trait, - do not have the trait or 0 doesn't matter if they have the trait or not. - App 2 selects group members, for a class project, according to how many members in the group should have a trait.
Some members have the trait (S), no members have the trait (0), or all members have the trait (A).
- App 1 selects group members, for a class project, according to the traits you believe a good group member should have.
- Let students decide which of the two Apps they would like to use to rate the traits. Put students in pairs or small groups according to the App they select.
- Rate the traits in the table on the lab notes page.
- Discuss.
Invention
- Tell. Select five traits, write them on the lab notes and write how many people in your group you would want with the trait, (o, 1, 2, 3, or 4).
- Share and discuss.
- Tell students the will have an opportunity to think about the roles and traits members have in a team activity next.
- Introduce next activity as an opportunity to see relationships in action during a group problem solving activity.
Activity 7 - Peer relationships in problem solving groups
- Select a group problem solving activity. Possible source: team building activities. Three possible selections.
- How Many Squares? Puzzle. or Forty Squares Puzzle (Easy preparation). See Teaching notes and Printable directions for students
- Five squares puzzle. Initial preparation requires printed directions and square patterns reproduced and put in an envelop for each student see Planning notes
- Board walking. Very good for outside activity. Requires preparation of boards. See planning information.
Focus questions:
- What is important for group members to know for groups or teams to work together to increase productivity, creativity, and cooperation?
Learning outcomes:
- Group members must feel psychologically safe
Suggested procedures overview:
- Ask focus question. What is important for group members to know for groups or teams to work together to increase productivity, creativity, and cooperation?
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and have them do a problem solving activity.
- Process the activity by listing what actions and behaviors led to success or hindered success.
Exploration
- Ask. What is important for group members to know for groups or teams to work together to increase productivity, creativity, and cooperation?
- Tell.
 (2016) did a massive investigation to discover what was the most important element for team work to increase productivity, creativity, and cooperation. They found it was psychological safety. Source
(2016) did a massive investigation to discover what was the most important element for team work to increase productivity, creativity, and cooperation. They found it was psychological safety. Source - Tell. You are going to do a group problem solving activity and
- Think about the actions and behaviors group member use solving the group problem and which are helpful and which are not helpful for group success.
- Introduce and do a group problem solving activity. Suggestions in the materials list at the beginning of this lesson.
Invention
- Distribute the Lab notes
- Ask. What actions and behaviors that were not helpful for the group to be successful? and what actions and behaviors helped the group to be successful?
- Write ideas in the lab notes.
Activity 8 - Assertive survey
Materials:
Focus questions:
- When is it good to be assertive?
- How does being assertive affect relationships?
Learning outcomes:
- Describe when it is appropriate to be assertive.
Suggested procedures overview:
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and assess their initial understanding of the focus questions.
- Ask when it is appropriate to stand up for your rights and be assertive.
- Fill out survey to rate assertiveness in different situations and discuss.
- Review situations is which to be assertive or to yield from an assertive response.
- Students select situations they feel are appropriate to be assertive or to yield to an assertive response.
Exploration
- Put students in pairs or groups of three or four.
- Ask. When is it good to be assertive? Accept all reasonable answers. When something is not safe. When a person asks you to do something you feel isn't right or legal. When don't want to do something. When something is against the rules.
- Distribute the Lab notes
Invention
- Ask. How assertive are you? Accept all reasonable answers.
- Tell. The lab notes has a survey for you to think about how assertive you are in certain situations.
- Rate each of the 15 situations as 4 strongly agree, 3 agree, 2 disagree, & 1 strongly disagree
- Discuss. How hard it is to be assertive, stand up for your rights, and to say no?
- Ask. What makes it harder to be assertive ... ? Accept all reasonable answers. Telling someone you like that you don't want to do what they are suggesting. Sometimes things that you shouldn't sound like they would be fun or exciting to do. Sometimes don't know how to do otherwise.
- Tell. The more a person stands up for their rights or is assertive or says no to something the next time it is easier.
- SO lets look at ideas for standing up for your rights and being assertive.
- Identify four situations that you think are most important for you to be assertive.
- Ideas from Stand up for your rights fact sheet or other ideas that are reasonable.
- Identify four situations that you think are most important for you to yield to another person's assertive response.
- Ideas from Stand up for your rights fact sheet or other ideas that are reasonable.
Activity 9 - Social skill role play. Use a social skill procedure to write a script and role play listening & standing up for your rights
Materials:
This plan first models how to use the social skill, listening, to write a script and role play an example for listening to a joke. Next it describes how to let students use the procedure, standing up for your rights and being assertive, to write a script and role play it use in a social situation.
The plan could be modified by assigning different social skills for each group or let students select from the 50 plus skills or they could draw a skill from a hat that you preselected and put on slips of papers for each group to choose from the hat.
- Stand up for your rights and Being assertive - fact sheet
- Procedure, script, and role play - lab notes
- Communicating well - fact sheet
- Social skills, listening procedure - fact sheet
- Learning social skills and procedures for 50 plus pro skills
Focus questions:
- How to people respond well in social situations?
Learning outcomes:
- Role play social skills: Listening to a joke & standing up for your rights, being assertive.
Suggested procedures overview:
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and assess their initial understanding of the focus question: How to people respond well in social situations?
- Walk through using a social skill to write a script for a role play to be a good listener for a joke.
- Use a social skill to write a script for a role play to stand up for your rights and be assertive.
- Share role play with class.
- Evaluate group work and presentation with scenario activity scoring guide.
Exploration
- Put students in pairs or groups of three or four.
- Distribute the Lab notes
- Tell. Building and maintaining relationships depends on good communication and social skills.
- Ask. How do people respond well in social situations? Accept all reasonable answers. Making good decisions and knowing how to communicate and different procedures that are appropriate. Procedures they learn from experience, from observing parents, video, reading about characters in social situations, thinking about situations and using metacognition, self talk, and role play to prepare and practice for certain situations.
Invention
- Tell. Class, later you are going to write a script and role play for being assertive that uses an assertive social skill.
- However, before you do that let's walk through an example for listening.
Script and role play walk through. See finished script 1 & script 2.
- I selected Listening, the first social skill from a list of 50 pro social skills.
- Need to know a setting where the skill will be used so I selected ... Listening to a joke.
- Then ask if a good decision was made and what social skill would be appropriate to implement and select the social skill.
- Then, remember what you learned and included in your communicating well guidelines and reflect on what might be helpful.
- I considered all ideas from my guidelines and decided the first six would fit well with listening.
- Be open minded - don't jump to conclusions
- Be courteous and respectful
- Use appropriate body language and mannerisms
- Listen
- Use wait time
- Be thoughtful
- Use clear concise language,
- Establish a purpose and make it clear
- Know your audience
- Define terms
- Check for understanding. Repeat what you think you understand.
- Ask questions
- Use I statements to express feelings
- Identify social skills as necessary to review and develop procedures for better communication.
- Next, I looked at the procedures for listening and decided listening for a short time, not long, could be used to make a procedure for listening to a joke and created a listening to a joke procedure:
- Listening to a joke procedure.
- Get prepared to listen by:
- Reflecting on your decision to listen to see if it is a good decision.
- Reflect on your communication skills and use self-talk to review what to do for better communication.
- Self talk. Remember to be open minded, courteous, respectful, act like I am interested and let my body know it, listen, be thoughtful and wait to laugh.
- Begin listening skill procedure
- Look at the person.
- Smile.
- Lean forward
- Do not interrupt
- Nod in agreement as appropriate
- Respond to their answers with a comment without changing the subject.
- Wait. If no response think about changing the subject.
- Groan, laugh, or ...
- Get prepared to listen by:
- Then I select some jokes to listen to.
- Why did the can crusher quit his job? Because it was soda pressing.
- How many apples grow on a tree? All of them.
- Why did a scarecrow win an award? Because it was outstanding in its field.
- Why do bees hum? Because they don't know the words.
- Why don't skeletons go trick or treating? Because they have no body to go with.
- Why can't you have nose 12 inches long? Because it would be a foot.
- What do you call cheese that isn't your? Nacho cheese.
- Why can't a bicycle stand by itself? It is two tired.
- And put it all together to get a script to use for a role play for telling and listening to a joke:
- Look at the person.
- Smile.
- Lean forward
- Do not interrupt
- Nod in agreement as appropriate
- Put students in pairs and have them use the script to role play. Let each pair be person 1 and person 2.
- Discuss.
- Ask. Are you ready to write your script for using the social skill being assertive?
- When, ready, go to discovery.
Writing a script for the role play: Telling and Listening to a Joke
Person 1. Want to hear a joke?
Person 2. [Mental thought pose.]
Self talk out loud. Do I want to listen to a friend's joke?
Did I make a good decision ? What social skill will I implement?
Um... communication skills . What to do for better communication and listening social skill adapted for listening to a joke social skill procedure.
Say. Yes.
Self talk out loud. Remember to be open minded, courteous, respectful, act like I am interested and let my body know it, listen, be thoughtful and wait to laugh.
[Execute joke social skill procedure:
]
Person 1. Why did a scarecrow win an award?
Person 2. Why did a scarecrow win an award?
Person 1. Because it was outstanding in its field.
Person 2. Groan ... Chuckle ...
Person 2. That was ... Have another one?
Person 1. ...
Discover
Assign social skills
- Put students in pairs or small groups of three or four.
- Select a setting for being assertive.
- Provide students with the Stand up for your rights and being assertive fact sheet.
- Review fact sheet for Standing up for your rights and being assertive. If want to add additional variations for more variety can also select from: saying no, disagree appropriately, report peer behavior, resist peer pressure, get a teacher's attention, or other categories from the social skills.
- Tell. Review a procedure for your chosen social skill.
- Use the Stand up for your rights and being assertive procedure to create a script for a social skill to role play a situation and present to the class.
Possible settings and situations: - Want to sit and eat lunch with a classmate that you don't usually so you can talk about something you are interested in related to a class discussion, but a person you usually sit with doesn't want you to sit with them.
- A peer asks you to come over and play video games. You want to do something with them, but you don't want to play a video game.
- Want to finish [book, homework, video game, ...] but a [family member, peer, ...] wants you to go with them to [watch a video, play a game, go ... ]
- Use the scenario activity scoring guide to evaluate each person's group work and presentation.
Activity - Crossword puzzle
Materials:
Inclued three crossword puzzles: 1. warm-up includes more recognized half of words in word bank. 2. expert includes less recognized half or words in word bank. 3. brain-teaser includes all words in word bank.
Focus questions:
- How well do you know vocabulary of mental and emotional health?
Learning outcomes:
- Use word bank to solve a cross word puzzle.
Suggested procedures overview:
- Ask. How well do you know vocabulary of mental and emotional health?
- Share word list and crossword puzzles in lab notes.
- Let students work in groups to solve the puzzles.
Scoring guide for crossword puzzles
Top level
- 100% complete and correct
- 100% complete and 90% or more correct
- 90% complete and 80% or more correct
- Less than 80% complete
Lower level
Exploration
- Ask. How well do you know vocabulary of mental and emotional health?
- You can work in groups to review the vocabulary in the word bank and to complete a crossword puzzle.
- You may select from one of the three: warm-up, expert, or brain-teaser.
Invention
- What questions do you have about the puzzles?
- What was your experience with the vocabulary?
- What did you learn about doing crossword puzzles?
Lab Notes
Brainstorm: What makes healthy relationships?
- Accept all suggestions (no criticism).
- Free wheeling or hitch-hiking is allowed and encouraged.
- Generate a large number of ideas.
- Combinations and improvements are sought.
- Everyone says their idea out loud and each writes their own ideas.
- The wilder the idea the better.
What are relationships?
What makes a healthy relationship?
How do people nurture healthy relationships?
Learning goals:
Healthy Relationships (Activity 1)
Purpose - To describe healthy relationships
Directions: 1. Review the fact sheet with ideas for healthy relationships, 2. Categorize these 16 actions, 3. Write personal goals you use or would like to use for positive relationships. & 4. Describe how relationships affect the areas of health.
2. Categorize each as: helpful (+), unhelpful (-) , or neutral (0) for positive relationships
- _____ Pouts at little things.
- _____ Encourages everyone to work together.
- _____ Wants to be in a group according to friendships.
- _____ Communicates verbally and with body language.
- _____ Makes suggestions to help keep on task.
- _____ Reviews decisions and goals.
- _____ Blames others for their own mistakes.
- _____ Doesn't put down others or their ideas.
- _____ Solves conflicts with raised voice and demands their ideas be used.
- _____ Puts down other group member ideas.
- _____ Acts out instead of staying on task.
- _____ Threatens to quit or not participate.
- _____ Compliments self and others.
- _____ Accepts responsibility for their own actions.
- _____ Respects personal boundaries.
- _____ Respects and values others.
- _____ .................................................. Insert one you think should have been included.
3. Write goals to describe characteristics you use or would like to use for healthy relationships
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.![]()
10.
4. Describe how relationships affects areas of health
Respect yourself and others (Activity 2)
Purpose - To describe characteristics of respecting yourself and others.
What do people do that suggests they respect themselves and others?
Self-esteem is the value, respect, and confidence you have for yourself.
Self-efficacy is the belief or understanding a person has in their ability to succeed in specific situations or accomplish a task.
Goals to respect yourself and others
Directions: Review the key ideas for respecting yourself and others and Write personal goals you use or would like to use to respect yourself and others for these categories.
- Needs (Maslow)
- Understand and have good self-esteem & self-efficacy
- Respect self, others, & environment
- Relationships
-
- Communicate
-
- Be assertive
-
- Social skills.
Communicate Well (Activity 3)
Purpose - To describe guidelines to communicate well.
Write your ideas on how people communicate well?
Directions: Review the key ideas for quality communications and Write guidelines to use for good communication.
Guidelines to communicate well
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Family Relationships (Activity 4)
Purpose - To describe relationships that maintain physical, social, and mental/ emotional safe and healthy family.
List an describe relationships maintain physical, social, and mental/ emotional safe and healthy families?
Directions: Review the key ideas for healthy family relationships and Identify and describe an idea for each category to maintain or improve relationships
Identify and describe an idea for each category to maintain or improve relationships
Peer relationships (Activity 5)
Purpose - To describe characteristics and procedures for safe and healthy peer relationships.
Directions: List some actions that encourage and discourage peer relationships.
Actions that encourage peer relationships:
Actions that discourage peer relationships:
Directions: Classify the following behaviors as positive (+), negative (-), or neutral (0) for relationship building.
- _____ Interrupts people when they talk.
- _____ Judges people by the way they look.
- _____ Continue to be them self in spite of what other people say.
- _____ Don't communicate truthfully, because it might hurt other people's feelings.
- _____ Threaten people to change their minds.
- _____ When in a bad mood or upset, walk away.
- _____ Use I statements when upset or in a bad mood.
- _____ Don't tell people when they interrupt.
- _____ Invite someone in your class group to sit with you at lunch to continue a conversation.
- _____ A person wants you to spend more time with them than other group members.
- _____ A person who doesn't want to share responsibility for completing an assignment.
- _____ Disagree even though it hurts another person's feelings.
- _____ Agree to respectfully disagree.
- _____ Blame others when something doesn't help in achieving the goal.
- _____ You feel forced to agree or comply to achieve a group goal.
- _____ A group member asks others for their thoughts and ideas.
Directions: Review the key ideas for peer relationships
Identify behaviors that build relationships.
Describe what a person should consider when considering expanding a relationship.
Describe how to maintain friendships when a friend chooses activities with others.
Describe your ideal group members (Activity 6)
Purpose - To describe traits for group members.
Directions: Choose direction number 1 or number 2 and complete the activity.
- App 1 selects group members, for a class project, according to the traits you believe a good group member should have.
+ have the trait, - do not have the trait or 0 doesn't matter if they have the trait or not. - App 2 selects group members, for a class project, according to how many members in the group should have a trait.
Some members have the trait (S), no members have the trait (0), or all members have the trait (A).
| Good listener ..... | Good listener ..... | Dominating ..... |
| Polite ..... | Makes fun of people ..... | Assertive ..... |
| Open minded ..... | One track mind ..... | Mean ..... |
| Leader ..... | Cold ..... | Passive ..... |
| Controlling ..... | Sincere ..... | Insecure ..... |
| Lazy ..... | Smart ..... | Rude ..... |
| Irresponsible ..... | Daredevil ..... | Serious ..... |
| Social ..... | Shy ..... | Manipulative ..... |
| Snob ..... | Considerate ..... | Immature ..... |
| Caring ..... | Bossy ..... | Fun loving ..... |
| Show off ..... | Ditsy ..... | Best friend ..... |
| Understanding ..... | Follower ..... | Opinionated ..... |
| Competitive ..... | Not dependable ..... | Good looking ..... |
| Reliable ..... | Outspoken ..... | Moody ..... |
| Pushes boundaries ..... | Impatient ..... | Responsible ..... |
| Trustworthy ..... | Needy ..... | Creative ..... |
| Annoying ..... | Happy ..... | Social ..... |
| Funny ..... | Pouty ..... | Likes music ..... |
| Likable ..... | Impatient ..... | Willing to change ..... |
| Loner ..... | Team player ..... | Like challenges ..... |
| Demanding ..... | Athletic ..... | Flirt ..... |
| Respects boundaries ..... | Self-centered ..... | Good student ..... |
| Procrastinator ..... |
You may add some traits of your own and rate them.
List five traits and the number of people in a group of four you would want with the trait.
(o, 1, 2, 3, or 4).
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Describe peer interactions in a cooperative group (Activity 7)
Purpose - To review actions and behaviors and and identify what is and is not helpful for group success.
![]() (2016) did a massive investigation to discover what was the most important element for team work to increase productivity, creativity, and cooperation. They found it was a psychological safety environment. Source
(2016) did a massive investigation to discover what was the most important element for team work to increase productivity, creativity, and cooperation. They found it was a psychological safety environment. Source
Directions: Participate in a group activity and answer the following questions.
What actions and behaviors were not helpful for the group to be successful?
What actions and behaviors helped the group to be successful?
Assertive survey (Activity 8)
Purpose - To review and reflect on the use of assertive and non assertive behaviors.
When is it appropriate to be assertive?
Directions: Rate each of the following according to how strong you agree with it.
Use a scale from 1-4.
..... 4 strongly agree ..... 3 agree ..... 2 disagree ..... 1 strongly disagree
- _____ When people hurt your feelings, you use an I statement to let them know how you feel.
- _____ If someone borrows something from me and doesn't return it the next day, I will remind them.
- _____ I tell people when I disagree with them even if it means they might not like it.
- _____ I ask for explanations in class when I don't understand something.
- _____ When someone explains something to me and I don't understand it, I ask them to clarify or I ask questions.
- _____ When a person makes a general remark or says someone said, I ask them to identify who it was specifically.
- _____ When it is clear that the class is not understanding an assignment and no one is saying so, I will speak up and say, I don't understand.
- _____ I tend to do what I think is right even when others might not.
- _____ I let people know when they disappoint me.
- _____ I say no when classmates want to copy my homework or test answers.
- _____ If a classmate is disturbing someone during class, I ask them to stop.
- _____ If I have a friend who does something I think is not in their best interest, I tell them how I feel about it.
- _____ If I need a favor, I will ask a friend.
- _____ When someone asks me to do something that goes against my values, I will refuse to do it.
- _____ I will express my ideas on things, even if others disagree.
Identify four situations that you think are most important for you to be assertive.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Identify four situations that you think are most important for you to yield to another person's assertive response.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Social skill role play (Activity 9)
Purpose - To review and practice the use of social skills.
How to people respond well in social situations?
Notes for procedure on listening to a joke.
Notes for listening to a joke role play.
Directions: Select a situation where you can be assertive with a decision you make or a group you are in makes. Use the procedure for being assertive or refusal to role play how you would leave or refuse to go along with another person or group. See stand up for your rights fact sheet
Procedure for being assertive:
Notes for being assertive role play.
Crossword Puzzles
Warm-up
Purpose - To review and practice the use of vocabulary related to healthy relationships in the word bank.
Directions: Review the words in the word bank and use them to complete the crossword puzzle.
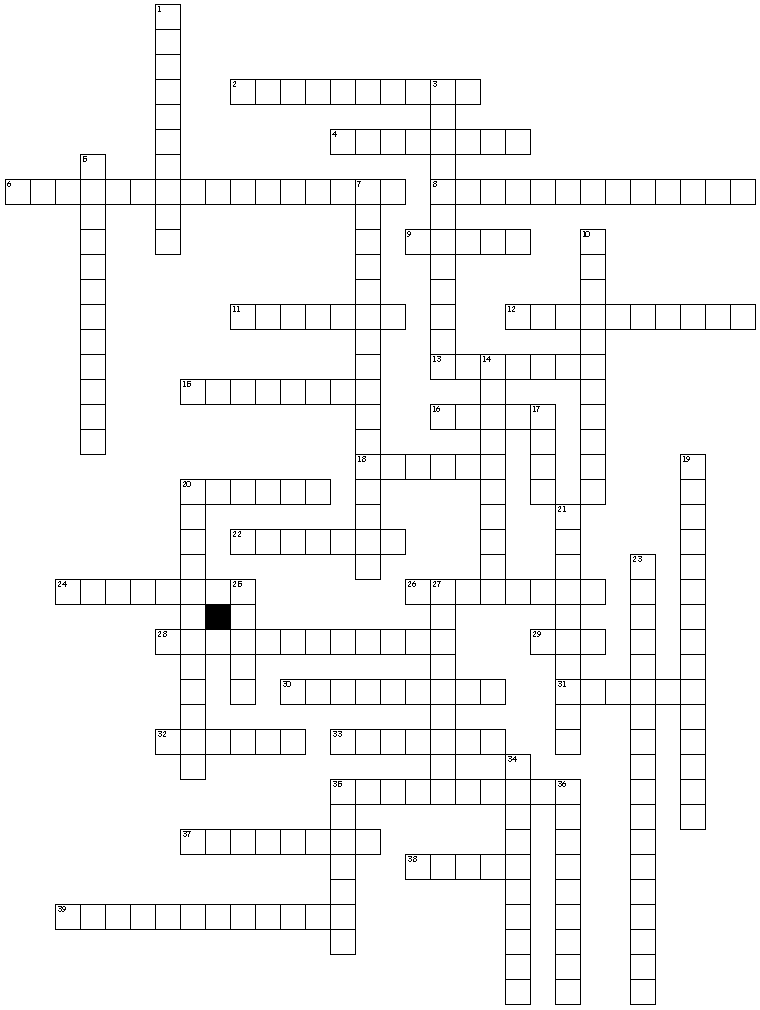
Across
2. an exaggerated oversimplified belief used to describe a group of people.
4. physical force used to harm or threaten a person or damage property.
6. an act of physical harm on one or more family members by another family member. (two words)
8. the necessities individuals need to achieve self-actualization. (two words)
9. all the different ways to communicate.
11. a brother or sister
12. a dishonest unfair way to influence or control other people.
13. to kick out, or restrict entry to a group.
15. a feeling of resentment or envy of another person or group.
16. is the act of promising money or a favorable act if a person performs or refrains from performing a specific task.
18. a favorable action or object is given after a specific action is or isn't completed.
20. to interact with others in a manner that treats them with consideration, respect, and kindness.
22. a legal end of a marriage.
24. is a disagreement, struggle, or fight between two or more individuals who must cooperate or fail.
26. an action that indicates violence, injury, or punishment will happen if a specific action is or isn't completed.
28. the manner in which people are connected.
29. acronym for the federal agency to control and prevent public health.
30. an unfavorable or favorable opinion or feeling formed without knowledge, thought, or reason.
31. the act of requiring a person to perform insulting, demeaning, or harmful tasks as entry requirements to a group.
32. includes grand parents, parents, brothers & sisters, aunts & uncles, cousins
33. failure to provide for a child's basic needs.
35. persistent negative interactions that pester, annoy, bother, harm, or torment others.
37. an act that deliberately intimidates, harms, or threatens another person.
38. the physical, emotional, mental, or sexual mistreatment of a person.
39. one person has custody and total care for one or more children. (two words)
Down
1. overly menacing, threatening, forceful, or pushy behavior to achieve a goal.
3. positive and negative influence same age people have on each other. (two words)
5. the belief or understanding a person has in their ability to succeed. (hyphenated word)
7. voluntary work intended for the common good, usually through an organized group. (two words)
10. the rights, privileges, and duties of a member of a nation.
14. any form of abuse directed at a child. (two words)
17. the desire to have something another person or group has.
19. organizations that give time, money, and other resources to provide goods or services to benefit others. (two words)
20. keeping information secret or private.
21. a relationship between people who know each other, trust, and support each other.
23. the process of ending a disagreement or conflict with cooperation and problem solving. (two words)
25. physical and verbal actions used to influence a person until a specific action is or isn't done.
27. a feeling of enjoyment, contentment, satisfaction, cheerfulness, joy, good spirits, and well-being.
34. the value, respect, and confidence you have for yourself. (hyphenated word)
35. open, fair, truthful, and honorable.
36. the ability to accept different beliefs and practices in a fair, objective, and caring manner.
Expert
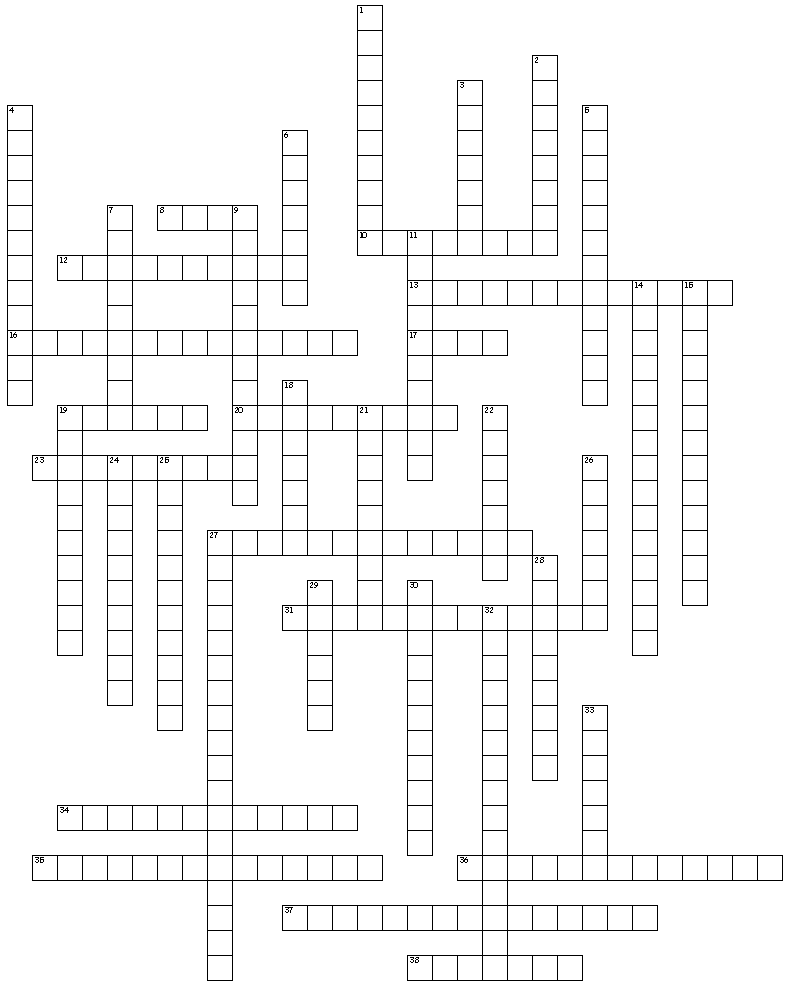
Across
8. an unfair comparison of something, someone, or group to another.
10. to increase in intensity or become more serious.
12. a household in which a child is raised by someone other than its natural or adoptive parent. (two words)
13. when two person's esteem or sense of worth is the same for each other. (two words)
16. parent or parents and one or more child of another parent. (two words)
17. the actions taken by a person in a particular social setting influenced by what they believe is appropriate or customary.
19. using a threat or harm if a specific action is or isn't completed.
20. an action that indicates violence or a payment will result as a consequence if a specific action is or isn't completed.
23. a way to focus a communication on your feelings instead of a person's behavior. (two words)
27. when a person or group tries to convince or force a decision or action others. (two words)
31. married parents and children from other parents. (two words)
34. places or organizations where young people go for leisurely or other group activities. (two words)
35. parents and children who live in a kinship group and function as a nuclear family with oher relatives: grandparents, cousins, aunts & uncles, in-laws, or close friends, and colleagues. (two words)
36. negotiation where the mediator is a peer of the people with the conflict. (two words)
37. the repeated use of violence and abusive behaviors passed on from one generation to the next. (three words)
38. the act of negotiating to influence them to do or not do a specific action.
Down
1. the abuse or neglect of older individuals. (two words)
2. the willful killing of a human by another human.
3. not favoring one person or idea over another.
4. the nonverbal expression communicated with: gestures like bobbing and nodding. (two words)
5. an agency or answering service where people get informed help with a personal problem, disaster, or emergency. (two words)
6. saying positive things to a person to influence them to do or not do a specific action.
7. communicate your ideas strong enough to achieve a goal, resolve a conflict, or respectfully state your objections.
9. abuse toward marriage partner. (two words)
11. settling a disagreement with mutual agreement.
14. keeping a promise or commitment made to another. (two words)
15. an exchange of ideas.
18. refraining from a reaction, communication, or expression of ones feelings and ideas when a response would be beneficial.
19. a pledge to enhance and make a relationship stronger.
21. use a neutral third party to guide a problem solving process to resolve a conflict to a mutual solution.
22. a threat of physical attack or attack.
24. a decision by a married couple to live apart.
25. an expression of recognition, support, and appreciation of what a person does.
26. the legal obligation to make decisions affecting a minor child's protection, care, and education.
27. a close relationship between members of opposite gender, but not romantic or sexual. (two words)
28. physical and verbal blame used to influence a person to do or not do a specific action. (two words)
29. a small exclusive group of people with similar interests and goals.
30. the process two parties use to communicate with each other to resolve a conflict or disagreement and reach a mutual solution.
32. use listening skills well. (two words)
33. all of a group’s goods, tools, ideas, beliefs, values, ideas, and roles they share and teach each other.
Comprehensive
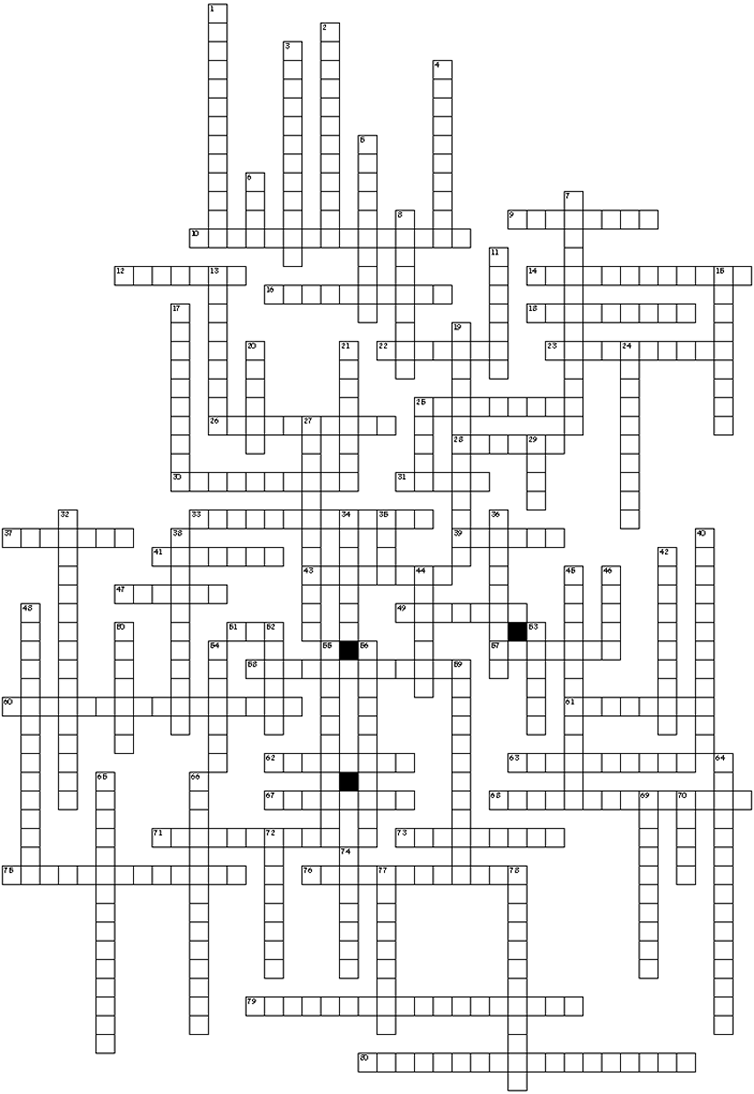
Across
9. a feeling of resentment or envy of another person or group.
10. keeping a promise or commitment made to another. (two words)
12. the act of negotiating to influence them to do or not do a specific action.
14. the nonverbal expression communicated with: gestures like bobbing and nodding. (two words)
16. overly menacing, threatening, forceful, pushy, or hostile to achieve a goal.
18. use a neutral third party to guide a problem solving process to resolve a conflict to a mutual solution.
22. a threat of physical attack or attack.
23. persistent negative interactions that pester, annoy, bother, harm, or torment others.
25. an action that indicates violence or a payment will result as a consequence if a specific action is or isn't completed.
26. the value, respect, and confidence you have for yourself. (hyphenated word)
28. a favorable action or object is given after a specific action is or isn't completed.
30. the abuse or neglect of older individuals. (two words)
31. physical and verbal actions used to influence a person until a specific action is or isn't done.
33. the necessities individuals need to achieve self-actualization. (two words)
37. a legal end of a marriage.
39. to interact with others in a manner that treats them with consideration, respect, and kindness.
41. a brother or sister
43. an act that deliberately intimidates, harms, or threatens another person.
47. the act of requiring a person to perform insulting, demeaning, or harmful tasks as entry requirements to a group.
49. the legal obligation to make decisions affecting a minor child's protection, care, and education.
51. acronym for the federal agency to control and prevent public health.
57. all of a group’s goods, tools, ideas, beliefs, values, ideas, and roles they share and teach each other.
58. the belief or understanding a person has in their ability to succeed. (hyphenated word)
60. an act of physical harm on one or more family members by another family member. (two words)
61. is a disagreement, struggle, or fight between two or more individuals who must cooperate or fail.
62. to increase in intensity or become more serious.
63. a dishonest unfair way to influence or control other people.
67. the willful killing of a human by another human.
68. parents and children who live in a kinship group and function as a nuclear family with oher relatives: grandparents, cousins, aunts & uncles, in-laws, or close friends, and colleagues. (two words)
71. a decision by a married couple to live apart.
73. communicate your ideas strong enough to achieve a goal, resolve a conflict, or respectfully state your objections.
75. negotiation where the mediator is a peer of the people with the conflict. (two words)
76. the manner in which people are connected.
79. a close relationship between members of opposite gender, but not romantic or sexual. (two words)
80. the process of ending a disagreement or conflict with cooperation and problem solving. (two words)
Down
1. when a person or group tries to convince or force a decision or action others. (two words)
2. keeping information secret or private.
3. one person has custody and total care for one or more children. (two words)
4. a pledge to enhance and make a relationship stronger.
5. settling a disagreement with mutual agreement.
6. an unfair comparison of something, someone, or group to another.
7. married parents and children from other parents. (two words)
8. a feeling of enjoyment, contentment, satisfaction, cheerfulness, joy, good spirits, and well-being.
11. open, fair, truthful, and honorable.
13. a way to focus a communication on your feelings instead of a person's behavior. (two words)
15. physical and verbal blame used to influence a person to do or not do a specific action. (two words)
17. any form of abuse directed at a child. (two words)
19. when two person's esteem or sense of worth is the same for each other. (two words)
20. includes grand parents, parents, brothers & sisters, aunts & uncles, cousins
21. physical force used to harm or threaten a person or damage property.
24. an exaggerated oversimplified belief used to describe a group of people.
25. is the act of promising money or a favorable act if a person performs or refrains from performing a specific task.
27. abuse toward marriage partner. (two words)
29. the actions taken by a person in a particular social setting influenced by what they believe is appropriate or customary.
32. voluntary work intended for the common good, usually through an organized group. (two words)
34. failure to provide for a child's basic needs.
35. the desire to have something another person or group has.
36. an unfavorable or favorable opinion or feeling formed without knowledge, thought, or reason.
38. the rights, privileges, and duties of a member of a nation.
40. an agency or answering service where people get informed help with a personal problem, disaster, or emergency. (two words)
42. a relationship between people who know each other, trust, and support each other.
44. not favoring one person or idea over another.
45. an exchange of ideas.
46. the physical, emotional, mental, or sexual mistreatment of a person.
48. the repeated use of violence and abusive behaviors passed on from one generation to the next. (three words)
50. refraining from a reaction, communication, or expression of ones feelings and ideas when a response would be beneficial.
52. using a threat or harm if a specific action is or isn't completed.
53. a small exclusive group of people with similar interests and goals.
54. to expel, kick out, prevent inclusion, or restrict entry to a group.
55. the process two parties use to communicate with each other to resolve a conflict or disagreement and reach a mutual solution.
56. an expression of recognition, support, and appreciation of what a person does.
59. places or organizations where young people go for leisurely or other group activities. (two words)
64. organizations that give time, money, and other resources to provide goods or services to benefit others. (two words)
65. use listening skills well. (two words)
66. parent or parents and one or more child of another parent. (two words)
69. a household in which a child is raised by someone other than its natural or adoptive parent. (two words)
70. all the different ways to communicate.
72. an action that indicates violence, injury, or punishment will happen if a specific action is or isn't completed.
74. saying positive things to a person to influence them to do or not do a specific action.
77. the ability to accept different beliefs and practices in a fair, objective, and caring manner.
78. positive and negative influence same age people have on each other. (two words)
Fact Sheets
Healthy relationship require
- Self-respect.
- Must respect yourself before you can respect others.
- Respect for others.
- Mutual trust
- Common goals (goal setting)
- Good decisions (decision making)
- Caring for your self and others
- Good family relationships
- Good peer relationships
- Realistic expectations
- Making and keeping commitments
- Knowing how to listen to other peoples ideas and read their emotions and feelings.
- Knowing how to communicate well. Both ideas and emotions.
- Good listening skills
- Good social skills
- Cooperation (social skill collaboration)
- Conflict resolution - Conflict resolution
- Share time
- Understanding different people and environments require different kinds of relationships.
- Good character. Traits people like other people to use to describe them. Like: trustworthy, loyal, helpful, friendly, courteous, kind, cheerful, caring, fair, responsible, respectful, and a good citizen. On your Personal Shield or Coat of Arms.
Respect yourself and others
Know how to have healthy relationships.
- Meet each others needs (Maslow - safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self actualization).
- Understand self-esteem and self-efficacy.
- Self-esteemis the value, respect, and confidence you have for yourself.
- Self-efficacy is the belief or understanding a person has in their ability to succeed in specific situations or accomplish a task.
Attributes that contribute to the perception of success or failure and affect self-esteem
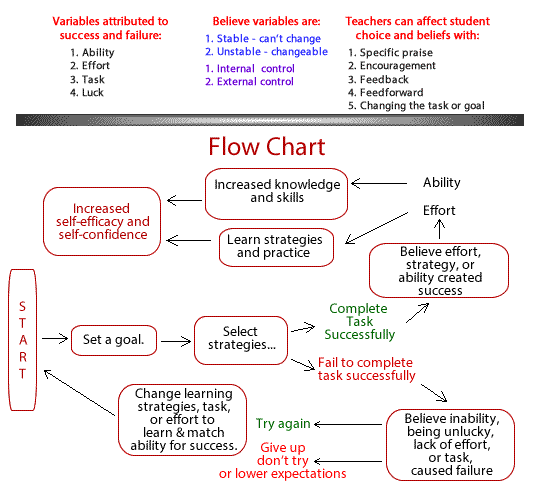
- Respect self, others, and relationships
- Personal identity - see activity Who am I? Personal Shield or Coat of Arms.
- Must know what character traits that you would like people to use to describe you. Like: trustworthy, loyal, helpful, friendly, courteous, kind, cheerful, caring, fair, responsible, respectful, and a good citizen.
- Develop good relationships
- Communicate well
- Be assertive
- Social skills
- Listening skills
- Other social skills for respectful interactions
Communicate Well
Guidelines for communicating well
- Be open minded - don't jump to conclusions
- Be courteous and respectful
- Use appropriate body language and mannerisms
- Listen
- Use wait time
- Be thoughtful
- Use clear concise language,
- Establish a purpose and make it clear
- Know your audience
- Define terms
- Check for understanding. Repeat what you think you understand.
- Ask questions
- Use I statements to express feelings
- Identify social skills as necessary to review and develop procedures for better communication.
Family Relationships
Ideas and behaviors related to stronger family relationships
- Provide for the physical needs and other Maslow's levels.
- Respect parents
- Commitment to establish a cohesive functional family where each is willing to provide time, sacrifice, and work together to solve problems and provide for each others physical, social, mental and emotional needs.
- Solve problems: related to marriage, illness, death, financial situations, moving, alcohol or drug abuse, emotional stress,
- Know family values, traditions, procedures, relationships
- Share similar values and ethics and trust in each other
- Good social skills
- Assist with tasks needed for family life
- Desire to cooperate and resolve conflict
- Respect all family members
- Desire to learn family history and culture
- Seek to discover the value of each family member
- Work to provide a safe and healthy environment and lifestyle. Seat belts, bike helmets, nutritious meals, poison and medication out of reach for young children, have and maintain co2 and smoke detectors,
- Set and maintain limits on behavior. Use of electronic devices, appropriate sleep, avoiding risky behaviors,
- Provide medical care: regular medical check ups, inoculations, dental care, vision care, skin care,
- Know when to seek or ask for help.
- Know different places to seek help: counseling services, support groups, crisis center, community shelters, hot lines, law enforcement, hospitals, clinics, rescue units, fire, faith communities.
- Take action against abuse with 3R's: recognize, resist, and report.
Peer Relationships
Peers spend time together who have similar interests, values, and beliefs.
- Relationships increase with honest, clear, and open communication. Communication implies listening to each other.
- Relationships grow stronger when sharing celebrations, disappointments, successes, goals, dreams, and concerns.
- Relationships grow with mutual respect, care, and support.
- Distinguish between casual peer relationships and close friendships.
- Recognize when to expand or reduce peer relationships and set and respect boundaries.
- When meeting a person for the first time (face to face or Online) be cautious. Don't share personal information, address, phone number, email address, don't agree to meeting in private places, don't agree to anything that makes you feel uncomfortable.
- Ideas to consider when thinking of expanding a relationship.
- Does the person care about your feelings and desires?
- Does the person support you when you need it?
- Does the person respect you, treat you fairly, do what you want to do and not always what they want to do?
- Do they share your interests?
- Do they accept and appreciate any differences between you and them?
- Are they consistent and steady with their friendship?
- Are they discrete with personal information and keep secrets and personal information confidential?
- Suggestions and ideas to consider to overcome or reduce jealous or envious thoughts and maintain friendship when a friend chooses activities with others or a slight occurs.
- Accept the feeling and recognize it as an emotional response to the anxiety of a potential loss.
- Consider your ability and social skills to develop and maintain the relationship in the first place as positive and repeatable. Value yourself for what you are and not who you know or the people who hang out with you.
- Accept it for what it is. Not what it might or could be. This kind of comparison can become an infinite loop of unrealistic possibilities by comparing yourself to other people or comparing one situation to another.
- Consider a real friend celebrates positive unique differences and the good things their friends experience, not lament their own personal lack of involvement.
- Remember the positives of the friendship. Consider a friend's action from their point of view and consider if their decision seems appropriate or a deliberate slight on the friendship. If so, be prepared to dissolve the friendship.
- Remember you don't need to choose to feel jealous, anxious, or angry. You control your response to your emotions. Review how to deal with stress...
- Consider the positives and negatives for the ways people respond to slights or jealousy in relationships:
- They insure them self the friendship is intact and strong, celebrate the friends opportunity, and continue with the friendship as it unfolds.
- They feel threatened and attempt to increase control over the other person to strengthen the relationship.
- They withdraw from the relationship to avoid possible future situations of not being included.
Listening
- Look at the person.
- Smile.
- Lean forward
- Do not interrupt
- Nod in agreement as appropriate
- Respond to their answers with a comment without changing the subject.
- Wait. If no response think about changing the subject.
Listening for longer periods of time
- Sit when possible. Ask the person to sit and chat or talk.
- Look at the person, lean forward, make eye contact, bob and nod, don't interrupt, wait for appropriate time to respond or ask questions.
- Take notes or jot down ideas to remember later.
- Communicate interest. Say go on, I understand, I see ...
- Restate or repeat what you are hearing by rephrasing when possible to summarize.
- Check for understanding by summarizing...
- Ask questions. Ask for examples or say, the way I understand what you are saying is ...
- Communicate empathy.
- Communicate positive body language. Gestures like bobbing and nodding, hand on chin; open body language like hands open, arms not folded; facial expressions like smiling, eyes wide; posture that is erect, leaning forward; tone of voice like respectful, lower, slower, even pitch, matter of fact, slow deliberate rate.
- Provide feedback and feedforward. Explain how the communication is going and how it might be better.
Source Fifty social skills, procedures, charts, and sub skills.
Writing a script for the role play: Telling and Listening to a Joke
Person 1. Want to hear a joke?
Person 2. [Mental thought pose.]
Self talk out loud. Do I want to listen to a friend's joke?
Did I make a good decision ? What social skill will I implement?
Um... communication skills . What to do for better communication and listening social skill adapted for listening to a joke social skill procedure.
Say. Yes.
Self talk out loud. Remember to be open minded, courteous, respectful, act like I am interested and let my body know it, listen, be thoughtful and wait to laugh.
[Execute joke social skill procedure:
]
- Look at the person.
- Smile.
- Lean forward
- Do not interrupt
- Nod in agreement as appropriate
Person 1. Why did a scarecrow win an award?
Person 2. Why did a scarecrow win an award?
Person 1. Because it was outstanding in its field.
Person 2. Groan ... Chuckle ...
Person 2. That was ... Have another one?
Person 1. ...
Stand up for your rights (27)
Source
Everyone in a democracy has a right to communicate: to express their thoughts, feelings, and values openly and directly with consideration of the rights of others to do the same.
This relates historically to our:
- Declaration of Independence (1776) claim of a right to: life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness.
- The First Amendment in the Bill of Rights (1791) right of: free exercise of religion, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, right to peaceably assemble, and petition government to redress grievances.
For a person to claim these rights, it sometimes requires them to be assertive, sometimes in a conflict. There are four ways to handle a conflict situation: smoothing, win-lose, compromise, or withdraw. All may require an assertive response.
Situations when assertive responses can be appropriate:
Source: page 38.
- To make decisions
- To be treated with respect
- To refuse a request
- To make a mistake
- To change your mind
- To take time to consider requests
- To make reasonable requests
- To hold personal opinions
- To control your own destiny
- To express your feelings
Situation in which you should yield to an assertive response:
- To allow others to make their decisions
- To treat others with respect
- To consider the feelings of others
- To allow others to control their destiny
- To respect the opinions of others
- To not impose upon others
- To allow others the courtesy to consider requests.
- To act reasonably
- To ensure mistakes do not harm others
- To refuse courteously and assertively
Source: page 38.
- Review your decision and plan how to state your position clearly and respectfully.
- Provide an honest powerful reason to support it. Support includes:
- How your needs will be met by your decision
- How a different response will not meet your needs or goes against your values or breaks a promise to yourself or others.
- Could use an I statements and avoid you statements, you are ... you always ...
- Don't exaggerate or use emotional words like always, never, craziest, dumbest, ...
- Say no or state your intended response in a normal conversational tone. Support your statements with appropriate body language. Stand tall, relax and look the person in the eye or forehead. Don't look down. Shake your head no. Hold up hands with palms out and fingers up making the universal sign for stop. Or you may begin to turn away or execute your intended response.
- May want to suggest alternatives.
- Stand your ground. Can repeat your stand or decision again with strong body language and determination. Maintain eye contact, but do not make physical contact.
- If necessary, repeat again to show your resolve. May repeatedly shake head to signal no and begin to initiate your leave response.
- If it is necessary to leave, state you are going, if it is appropriate: home, school, and what you will do. If appropriate invite the person to go with you.
Note -while being aggressive and using a loud boisterous verbal tone or physical contact of pushing or shoving can sometimes be used to get your way, it can cause the other person to react negatively. They can become physical or aggressive or react passively doing nothing or initiate revenge later.
Accurate and quality information is needed to make good healthy decisions.
A healthy person understanding what is human, their body, it's anatomy, functions of life, growth, and development well enough to care for them self and others to attain and maintain physically, emotionally, and socially healthy bodies. To achieve this one must be able to describe, analyze, predict, and compare how different variables affect the body to make wise decisions. Desire to learn about nutrition, diet, exercise, sleep, stress, relaxation, choice of behaviors, social skills, conflict resolution, cooperation, genetics, safety, injuries, health status, illness, natural disasters, environmental health, and risks, will impact them and others in different situations or conditions.
Word bank
Abuse is the physical, emotional, mental, or sexual mistreatment of a person caused by an action or neglect of action.
Active listening see listening skills
Affirmation is an expression of recognition, support, and appreciation of what a person does. Affirm and celebrate behaviors that assist or help others or behaviors that are successful in achieving desired goals.
Aggressive is being overly menacing, threatening, forceful, pushy, or hostile to achieve a goal.
Assertive is clearly, respectfully, and confidently communicating your ideas and feelings strong enough to achieve a goal, resolve a conflict, or to respectfully state your objections.
Assault is a threat of physical attack or an actual sudden violent attack.
Bias 1: an unfair comparison of one thing, person, or group to another 2: a known or unknown tendency or preference for a particular idea, brand, result, or perspective that interferes with being impartial, unprejudiced, or objective when making a decision. 3: unfairly support one idea or side against another.
Ways bias can be used to influence decision making.
- With limited options or omission. Selections that offer one point of view by omitting alternatives. Offering only positive consequences and not negative.
- Placement Information given first or reported on the first page, or beginning of a television or radio newscasts.
- Use of photos, word selection in captions, camera angles, color, choice of shots.
- Use of names and titles. Mr. Mrs, Dr. ex-con, terrorist, freedom fighter, ...
- Use of numbers and statistics to make something a disaster report A hundred injured in air crash rather than only minor injuries in air crash.
- Selection of information source. A reporter, eyewitness, police, fire official, executive, elected or appointed government officials.
- Word choice and tone. Use of positive or negative words or words with a particular connotation. Riots, demonstrations, sit-ins, ribbon cuttings, speeches, ceremonies, gathering.
Body language is the nonverbal expression communicated with: gestures like bobbing and nodding, hand on chin; open body language like hands open, arms not folded; facial expressions like smiling, eyes wide; posture that is erect, leaning forward; tone of voice like lower, slower, even pitch, matter of fact;
Bullying is an act that deliberately intimidates, harms, or threatens another person.
Caring is to interact with and help other people in a manner that treats them with consideration, respect, and kindness.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is a federal agency in Atlanta, Georgia that tracks and investigates public health concerns and supports health through promotion, prevention and preparation activities to improve overall public health.
Child abuse is any form of abuse directed at a child.
Citizenship is the rights, privileges, and duties of a member of the community in which they are entitled to citizenship. In the United States by birth or through a legal process. Becoming a citizen of the United States process for naturalization.
Clique is a small exclusive group of people with similar interests and goals who may or may not actively exclude or demean people who are different or have different interests and goals.
Commitment is to pledge to contribute to a relationship in a manner to enhance and make it stronger.
Communication in a relationship goes beyond an exchange of ideas to include sharing each others feelings, thoughts, beliefs, expectations, and goals.
Community service is voluntary work intended for the common good, usually done through an organized group: school or college program or court ordered instead of imprisonment.
Confidential is keeping information given secret or private.
Conflict is any contradiction, disagreement, struggle, or fight that can be interpersonal or internal. Interpersonal conflict is when two or more individuals who must cooperate together fail to share the same views, interests, or goals. Internal conflict is within an individual. See conflict resolution and mediation
- Power struggle is when a person or group tries to convince or force their decision or action over those of the other person or group.
- Personal loyalty is keeping a promise or commitment made to another person or group.
- Jealous or envy is a feeling of resentment or envy of another person or group. Envy is the desire to have something another person or group has. See ideas for coping with jealousy & envy.
- Property disputes is a disagreement over the owner ship of physical objects.
- Conflicting opinion, values, beliefs, ethics is when another person or group has different opinions, values, beliefs, or ethical ideas than yours.
- Lack respect and caring disrespect by being rude, bullying, putting another person down, making fun of them or treating them bad in anyway.
Conflict resolution is the process of ending a disagreement, conflict, with cooperation and problem solving. See conflict resolution and mediation
Compromise is settling a disagreement with mutual agreement. Often with both parties giving up something and neither getting what they want. A win-win solution is better when one can be achieved. See conflict resolution and win-win, win-lose, & lose-lose chart
Crisis center is a central building, agency, facility, answering service, ... where people get informed help or advice with a personal problem or receive information during a disaster or emergency.
Culture is the total of a groups goods, tools, ideas, beliefs, values, ideas about time, and roles that people communicate, share, and teach to each other. See iceberg model of culture.
Custody is the legal obligation to make decisions affecting a minor child's protection, care, and education, usually with respect to a divorce or separation.
Cycle of violence is the repeated use of violence and abusive behaviors passed on from one generation to the next.
Divorce is a legal end of a marriage according to established law.
Domestic violence is an act of physical harm on one or more family member by another family member.
Elder abuse is the abuse or neglect of older individuals.
Escalate is to increase in intensity or become more serious.
Exclude to expel, kick out, prevent inclusion, or restrict entry to a group.
Family - Grand parents, parents, brothers & sisters, aunts & uncles, cousins
- Adoptive family is parent or parents and one or more adopted children. May also include biological children.
- Blended family is married parents and children who can include children of the parents, but also include children from previous marriages.
- Extended family is parents and children who live in a kinship group and function as a nuclear family. May include various relatives: grandparents, cousins, aunts & uncles, in-laws, or close friends, and colleagues.
- Foster home is a household in which a child is raised by someone other than its natural or adoptive parent. There may also be other children who may be the parents biological children, blended, adopted or also under foster care.
- Single-parent family is one parent has custody or total care for one or more children. Caused by divorce, separation, or death.
Foster home is a household in which a child is raised by someone other than its natural or adoptive parent. There may also be other children who may be the parents biological children, blended, adopted or also under foster care.
Friendship is a relationship between people who know each other, trust, and support each other. Usually in a caring manner, which develops a bond of mutual affection.
Happiness is the feeling of enjoyment, contentment, satisfaction, cheerfulness, joy, good spirits, and well-being. The search for happiness is one of the chief sources of unhappiness. Eric Hoffer. In other words. The pursuit of happiness is good. However, the more people think about how happy they are and how to increase their happiness, the less likely they are to actually feel happy.
Harassment is persistent negative interactions that pester, annoy, bother, harm, or torment others.
Hazing is the act of requiring a person to perform insulting, demeaning, or harmful tasks or rituals as entry requirements to become a member of a certain group.
Honesty is being open, fair, truthful, and honorable.
Homicide is the willful killing of a human by another human.
I messages or I statements is a way to focus a communication on your feelings instead of a person's behavior. See I statements.
Listening skills or active listening is paying close attention to what someone is communicating vocally and emotionally with body language.
Manipulate is a dishonest unfair way to influence or control other people. The following are ways to manipulate
- Threaten is an action that indicates violence, injury, or punishment will result in retaliation if a specific action is or isn't completed.
- Blackmail is an action that indicates violence or a payment will result as a consequence if a specific action is or isn't completed.
- Reward is the act of allowing a favorable action or giving a favorable object as consequence if a specific action is or isn't completed.
- Coerce is the act of with holding a favorable action or favorable object or using a threat or harm if a specific action is or isn't completed.
- Mock or tease is the act of physical and verbal actions used to influence a person until a specific action is or isn't done.
- Guilt trip is the act of physical and verbal blame used to influence a person to perform or not to perform a specific action.
- Bargain is the act of negotiating with a person to influence them to perform or refrain from performing a specific action.
- Flatter is the act of saying positive things to a person to influence them to perform or refrain from performing a specific action.
- Bribe is the act of promising money or a favorable act if a person performs or refrains from performing a specific task.
Media is all the different ways together of mass communication: Internet, web sites, television, radio, newspapers, magazines, books, ...
Mediation the use of a neutral third party to guide a problem solving process to resolve a conflict or disagreement and reach a mutual solution. See conflict resolution and mediation
Mutual respect is when a person's esteem or sense of worth is the same for each other.
Neglect is the failure to provide for a child's basic needs.
Negotiation is the process two parties use to communicate with each other their differences in a problem solving process to resolve the conflict or disagreement and reach a mutual solution through discussion. See conflict resolution and mediation
Neutral is not favoring one person or idea over another.
Passive is refraining from a reaction, communication, or expression of ones feelings and ideas when a response would usually be beneficial.
Peer mediation is mediation where the mediator is a peer of the people with the conflict. See mediation.
Peer pressure the positive and negative influence same age people have on each other.
Personal needs are the necessities: food, water, air, safe environment (shelter plus), social needs, physiological dependence, psychological dependence, esteem, and self-actualization.
Platonic friendship is a close relationship between members of opposite gender, but not romantic or sexual in nature.
Prejudice is an unfavorable or favorable opinion or feeling formed without knowledge, thought, or reason. Often regarding an ethnic, racial, social, or religious group.
Relationship is the manner in which people are connected. Relationships will vary according to who you interact with and where the interactions take place: home - family, school - peers, teachers, counselors... community - friends, customer representatives, sales people, strangers, ...
Role is the actions taken by a person in a particular social setting influenced by what they believe is appropriate or customary.
Self-efficacy is the belief or understanding a person has in their ability to succeed in specific situations or accomplish a task.
Self-esteem is the value, respect, and confidence you have for yourself.
Separation is a decision by a married couple to live apart from each other.
Sibling is a brother or sister
Spousal abuse is any form of abuse toward a spouse (marriage partner).
Stereotype is an exaggerated oversimplified belief or idea that is known collectively by a group of people and used to describe a group of people. Like patriot, American Indian, cowboy, jock, nerd...
Tolerance is the ability to accept different beliefs and practices in a fair, objective, and caring manner.
Youth centers are places or organizations where young people go for leisurely or other group activities.
Violence is swift physical force used to harm or threaten a person or damage property.
Volunteer groups are groups and organizations that give time, money, and other resources to provide goods or services to benefit others.