Development of Physical Fitness Plans
(middle grades)
Activity and Lesson plan
Overview
Decisions are often made subconsciously and emotionally without sufficient investigation or critical thinking. The purpose of these activities, is to provide guidance in the awareness of a need to set physical fitness goals and develop a physical fitness program to implement and achieve them to live a healthy life.
It is helpful to have previously completed the activities for:
Background information:
Planning information
Learner background information
A plan designed for learners who have prior knowledge in goal setting, decision making, and working in groups.
General information on planning
Intended learnings & learners thinkings
Big ideas, concepts, facts, and outcomes
Big idea
Health is enhanced when healthy goals are identified, set, and implemented to improve physical fitness.
Related concepts and facts
Physical fitness is being able to be active in our everyday life without an unhealthy amount of stress and strain on our body so we might perform our everyday activities without being overly tired or worn down.
Outcome
Write a physical fitness plan, implement it for a required period of time, and set goals to continue.
Specific outcomes - Standard 3
Learners will demonstrate the ability to access valid information and products and services to enhance health.
3.12.1 Evaluate the validity of health information, products, and services.
3.12.2 Utilize resources from home, school, and community that provide valid health information.
3.12.3 Determine the accessibility of products and services that enhance health.
3.12.4 Determine when professional health services may be required.
3.12.5 Access valid and reliable health products and services.
Specific outcomes - Standard 6
Learners will demonstrate the ability to use goal-setting skills to enhance health.
6.12.1 Assess personal health practices and overall health status.
6.12.2 Develop a plan to attain a personal health goal that addresses strengths, needs, and risks.
6.12.3 Implement strategies and monitor progress in achieving a personal health goal.
6.12.4 Formulate an effective long-term personal health plan.
Specific outcomes - Standard 7
Learners will demonstrate the ability to practice health-enhancing behaviors and avoid or reduce risks.
7.12.1 Analyze the role of individual responsibility for enhancing health.
7.12.2 Demonstrate a variety of healthy practices and behaviors that will maintain or improve the health of self and others.
7.12.3 Demonstrate a variety of behaviors to avoid or reduce health risks to self and others.
Scoring guide suggestions (rubric)
Use valid information to set goals and choose behaviors for physical health.
Top level
- Choose mastery oriented behaviors that benefit a healthy body through a variety of activities that include a focus on process, accurate information, identification of a problem, analysis, generation of alternative behaviors and possible choices with positive and negative consequences to implement, and evaluate suggestions and describe benefits for a comprehensive physical health process.
- Behaviors include activities that include cardiorespiratory and muscular work outs with safe use of equipment. Perform mastery oriented behaviors that benefit a healthy body. However, do not understand different ways to vary their program to achieve similar results.
- Behaviors include more actions that put physical health at risk than (very little cardiorespiratory activity other than regular movement from place to place, little muscular work out, miss use of equipment, reckless activity that might endanger body, over eating, abuse alcohol or drugs, ...)
Lower level
Strategies to achieve educational learnings
Instructional procedures are based on learning cycle theory & method
Activity Sequence to provide sufficient opportunities for students to achieve the targeted outcomes.
- Focus learner's attention by asking the main focus question.
- If students aren't familiar with a goal setting process, present the four step goal setting process by asking:
- How do people make decisions? Go with their gut. React without thinking. Organize a process that follows a series of steps: Identify a problem, collect information, analyze the information, generate options or choices, consider consequences, make a decision, implement, evaluate .
- What influences their decisions? Their emotions, past experiences, values, parents, friends, desire, rewards ...
- What different options do they have that are available? They can make a decision based on a logical process, consider what other authority figures would suggest, seek help, listen to a friend's advice, ...
- How are options or choices determined? Brain storm, from past experiences, listening to what others suggest ...
- How are positive and negative consequences determined for the options? Brain storm, from past experiences, listening to what others suggest ...
- How are the options evaluated? With the consequences, ethics, legal, moral, and values applied to consequences and risks.
- Have learners high light ideas they feel are important to consider when setting goals.
- If they haven't used the goal setting process before, have them select a goal and complete the four step goal setting process for a goal to do something for a week. Like read 30 minutes each day, fix a meal, clean ... other ...
- Share their plans and let them edit them.
- Let them work on their plan for the week as you all work together to write their individual fitness plans.
- Share, discuss, and process results with scoring suggestions for their goal setting activity.
- Have students summarize the importance of knowing and using a goal setting process.
- Use the FITT Model and other activities that follow to begin to write a four step goal setting process to develop a fitness program.
- Intensity zones for cardiovascular fitness: Have students calculate their target heart rate for low, moderate, and highly intense zones.
- Learn how to accurately measure a pulse - Pulse for 10 secs and 6 secs....X by 6 & 10 to get the minute heart rate.
- Test areas of fitness:
Reaction Time - Counting in base 16 and meter stick test.
Flexibility - sit and reach test
Cardio Endurance - Mile test and step test.
Power - Vertical Jump
Muscular Strength - Max Bench Press, Grip strength
Muscular Endurance - Push up test, Sit up test
Body Composition - BMI Chart
Speed - 40 yard dash
Agility - Shuttle run or 3 cone drill. - Teamwork activity - five squares puzzle activity teacher notes. and Student materials, directions and puzzles.
- Review results of week long goal setting activity, discuss, and ask. Do you have enough information about goal setting and what kind of program you need to develop and maintain your physical fitness?
- If yes, help them complete their goal setting for physical fitness.
- IF not, ask and answer question still they are able to complete their goal setting for their fitness program.
- Have them begin their program and record notes about what they do for a week.
- After a week, review:
- Say. Whatever you think about your fitness program is totally okay to feel that way. It is important for you to review those feelings and and make changes until you feel comfortable with what you are doing.
- What criteria can you use to judge those feelings? Basically: will it work for my physical fitness and two are the activities ones that I will do reliably?
- Review what you actually did and decide if you need to make changes.
- Share and discuss in groups and as a class.
Focus question - When do people need to make decisions?
- How do people enhance their physical health?
- How do people set goals?
- What behaviors are beneficial for positive physical health?
- What different options are available to improve physical health?
- What options or choices are best for different people?
- How are the options evaluated?
- What goals and behaviors should be included in physical fitness programs?
Materials
- meter stick, notebook or folder, calculator, gravity, subject and experimenter.
- Lab notes
Lab Notes
PULSE CHART for 10 secs and 6 secs
Ten second count
- Find your pulse at your wrist.
- Make sure you can find it whenever you want it.
- Count the number of pulses you feel in exactly 10 seconds.
- Repeat this count four times, and record each one on the pulse chart below.
- Multiply each count by six to find the number of pulse beats per minute.
- Find your average pulse rate by adding the four numbers in the number of pulses per minute column and then dividing the total by four to find the average.
| Trial | Number of pulses in 10 seconds |
x 6 = | Number of pulses per minute |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | x 6 = | ||
| 2. | x 6 = | ||
| 3. | x 6 = | ||
| 4. | x 6 = | ||
| Add the pulses per minute together. = ____ |
_______ / 4 = ______ Average number of pulses per minute | ||
Six second count
- Find your pulse at your wrist.
- Make sure you can find it whenever you want it.
- Count the number of pulses you feel in exactly six seconds.
- Take this count three more times, and record each one on the pulse chart below.
- Multiply each count by 10 to find the number of pulse beats per minute.
- Find your average pulse rate by adding the four numbers in the number of pulses per minute column and then dividing the total by four to find the average.
| Trial | Number of pulses in 6 seconds |
x 10 = | Number of pulses per minute |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | x 10 = | ||
| 2. | x 10 = | ||
| 3. | x 10 = | ||
| 4. | x 10 = | ||
| Add the pulses per minute together. =____ | / 4 = ______ Average number of pulses per minute | ||
Target cardiovascular fitness
The target heart range is the ideal range during aerobic activity.
To calculate your target heart rate.
- Multiply your age by 0.7.
- Subtract this number from 208 to get an estimate of your maximum heart rate. (if you are 16 years old, your maximum heart rate would be 197 beats per minute.
- Multiply this number by 50 percent to get your minimum heart rate for moderately intense activity.
- Multiply the number in step 2 by 70 percent to get your maximum heart rate for moderately intense activity and the minimum for vigorous activity.
- Multiply the number in step 2 by 85 percent to get your maximum target heart rate for any physical activity. Exercising above this rate is dangerous.
- To figure your heart rate during exercise, take your pulse for six seconds and multiply it by 10.
Reaction Time - Counting to 10 16 in base sixteen
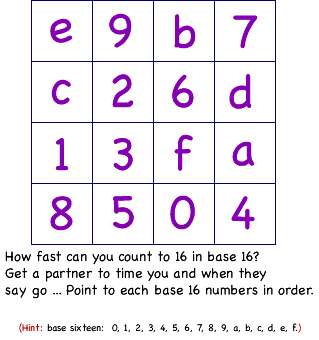
- See how fast you can complete the task and record the times.
- Record the first three and the last if you do it more than four times.
- Try it again tomorrow after you sleep on it and record those times.
| Time data by trials and comparison | Time in seconds |
|---|---|
| Day 1 - trial 1 | |
| Day 1 - trial 2 | |
| Day 1 - trial 3 | |
| Day 1 - trial last | |
| Difference between Day 1 trial 1 and Day 1 trial last |
|
| Day 2 - trial 1 | |
| Day 2 - trial 2 | |
| Day 2 - trial 3 | |
| Day 2 - trial last | |
| Difference between Day 2 trial 1 and Day 2 trial last |
|
| Difference between Day 1 best time and Day 2 best time |
What statements can be made about reaction time, sleeping, and learning?
Reaction Time Ruler Test
Materials : meter stick, notebook or folder, calculator, gravity, subject and experimenter.
Procedure:
- The person, whose reaction time is being test, sits at the edge of a table, resting their elbow on the table so their wrist extends over the side of the table with their hand positioned to catch the meter stick as soon as it is dropped.
- Another person holds a meter stick vertically above the subject's thumb and index finger so the zero edge of the meter stick is close, but not touching.
- When ready, drop the meter stick without warning.
- Record the centimeters the ruler fell before it was caught.
- Repeat several times (e.g.. 10 times) and find the average distance the meter stick dropped before it was caught.
- Use the table below to determine the time in seconds it took the ruler to fall over the measured distance in centimeters (cm).
- The formula: t = sqrt ( 2d / g ) is used to calculate time. d = the distance the ruler fell in meters, g = the acceleration of gravity in meters (9.8 m/s 2 ), and t = the time the ruler was falling in seconds.
1 cm = 0.045 s, 26 cm = 0.230 s, 51 cm = 0.323 s, 76 cm = 0.394 s,
2 cm = 0.064 s, 27 cm = 0.235 s, 52 cm = 0.326 s, 77 cm = 0.396 s,
3 cm = 0.078 s, 28 cm = 0.239 s, 53 cm = 0.329 s, 78 cm = 0.399 s,
4 cm = 0.090 s, 29 cm = 0.243 s, 54 cm = 0.332 s, 79 cm = 0.402 s,
5 cm = 0.101 s, 30 cm = 0.247 s, 55 cm = 0.335 s, 80 cm = 0.404 s,
6 cm = 0.111 s, 31 cm = 0.252 s, 56 cm = 0.338 s, 81 cm = 0.407 s,
7 cm = 0.120 s, 32 cm = 0.256 s, 57 cm = 0.341 s, 82 cm = 0.409 s,
8 cm = 0.128 s, 33 cm = 0.260 s, 58 cm = 0.344 s, 83 cm = 0.412 s,
9 cm = 0.136 s, 34 cm = 0.263 s, 59 cm = 0.347 s, 84 cm = 0.414 s,
10 cm = 0.143 s, 35 cm = 0.267 s, 60 cm = 0.350 s, 85 cm = 0.416 s,
11 cm = 0.150 s, 36 cm = 0.271 s, 61 cm = 0.353 s, 86 cm = 0.419 s,
12 cm = 0.156 s, 37 cm = 0.275 s, 62 cm = 0.356 s, 87 cm = 0.421 s,
13 cm = 0.163 s, 38 cm = 0.278 s, 63 cm = 0.359 s, 88 cm = 0.424 s,
14 cm = 0.169 s, 39 cm = 0.282 s, 64 cm = 0.361 s, 89 cm = 0.426 s,
15 cm = 0.175 s, 40 cm = 0.286 s, 65 cm = 0.364 s, 90 cm = 0.429 s,
16 cm = 0.181 s, 41 cm = 0.289 s, 66 cm = 0.367 s, 91 cm = 0.431 s,
17 cm = 0.186 s, 42 cm = 0.293 s, 67 cm = 0.370 s, 92 cm = 0.433 s,
18 cm = 0.192 s, 43 cm = 0.296 s, 68 cm = 0.373 s, 93 cm = 0.436 s,
19 cm = 0.197 s, 44 cm = 0.300 s, 69 cm = 0.375 s, 94 cm = 0.438 s,
20 cm = 0.202 s, 45 cm = 0.303 s, 70 cm = 0.378 s, 95 cm = 0.440 s,
21 cm = 0.207 s, 46 cm = 0.306 s, 71 cm = 0.381 s, 96 cm = 0.443 s,
22 cm = 0.212 s, 47 cm = 0.310 s, 72 cm = 0.383 s, 97 cm = 0.445 s,
23 cm = 0.217 s, 48 cm = 0.313 s, 73 cm = 0.386 s, 98 cm = 0.447 s,
24 cm = 0.221 s, 49 cm = 0.316 s, 74 cm = 0.389 s, 99 cm = 0.449 s,
25 cm = 0.226 s, 50 cm = 0.319 s, 75 cm = 0.391 s, 100 cm = 0.452 s
This test can be used to determine the reaction time for different situations. For example to a sound. The Apparatus can be used with the subject wearing a blindfold, and the meter stick being released at the same time as an auditory signal.
Physical fitness: F.I.T.T. Model
F.I.T.T. Model (Frequency, Intensity, Time and Type) identifies four important variables to consider when developing an exercise program.
- Frequency is how often to exercise. When considering frequency the amount of stress need to benefit from the work out needs to be considered along with the time the body needs to heal and build muscle and endurance.
- Intensity is the amount of effort or work for each specific exercise for a complete session or combination of sessions. Consider what is a good balance to provide an intense work out that will stress the body but not so difficult that it results in injury or burnout.
- Time is how long each session will last. Consider the intensity for each specific exercise performed: cardiovascular, resistance or both.
- Type refers to what system or part of the body each specific exercise will benefit: Will it benefit primarily cardiovascular, resistance training or both for each specific exercises performed.
Physical Fitness Review
Name______________________
Directions : Use a vocabulary term to answer each question.
- Cardiorespiratory
- Endurance
- Muscular Strength
- Muscular Endurance
- Flexibility
- Aerobic Exercise
- Anaerobic Exercise
- Warm-Up
- Exercise
- Sedentary
- Physical Fitness
- Physical Activity
-
Which Describes an intense, short burst of activity which muscles work very hard? ______________________
-
Which means the ability of your muscles to perform physical tasks over a period of time without tiring? __________________
-
Which is the ability of your heart, lungs, and blood vessels to send fuel and oxygen to your tissues during long periods of activity? ______________________________
-
Which is the amount of force your muscles can exert? ______________________________
-
Which describes the ability to move your body parts through their full range of motion? __________________________
-
Which defines all rhythmic activities that use large muscle groups for an extended period of time? _____________________________
-
Which is a gentle cardiovascular activity that prepares the muscles for work?________________________
-
Which is a form of movement that causes your body to use energy?_______________________
-
This is a lifestyle that involves little physical activity.____________________
-
Which is a purposeful activity that is planned, structured, and repetitive, and which improves or maintains physical fitness._________________________
-
This is the ability to carry out daily tasks easily and have enough energy to respond to unexpected demands. ______________________________
12-16. For each part of the F.I.T.T. Plan: write what each letter stands for, a definition, and give an example.
F _____________________
Definition:________________________________________________
Example:_________________________________________________
I _____________________
Definition:__________________________________________________
Example:__________________________________________________
T _____________________
Definition:___________________________________________________
Example:____________________________________________________
T _____________________
Example:____________________________________________________
Definition:____________________________________________________
16-21. List and Briefly explain the 3 stages of a workout.
Stages of a Workout
1.
2.
3.
21-30. Draw the Decision Making Circle and list the 9 steps to making a well thought out decision. In the following scenario - Go through the 9 steps and list examples of each in the circle to come up with the best decision.
Scenario : A friend asks you overnight and you know his parents are out of town. There are many options here - what path do you take?
30-40. Use the word back to identify the area of Fitness for each test to measure and then list one way to improve in that area.
Word Bank :
- Flexibility
- Body Composition
- Power
- Muscular Strength
- Agility
- Reaction Time
- Muscular Endurance
- Cardio Endurance
- Speed
Tests
Sit and Reach
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve
Grip
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve
Area of Fitness
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve
Ways to Improve
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve
60 Second Sit up
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve
Cone Shuttle
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve
BMI
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve
9 Minute Run
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve
Bench Max
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve
Vertical Jump
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve
Ruler Drop
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve
40 M Dash
- Area of Fitness
- Ways to Improve