Eye - Anatomy and seeing
The sweetest of all sounds is praise
Zenophon
Function
The eye is an organ able to receive light. Images we sense travels from the eye as electrochemical signals to the brain where they are interpreted. The signals can be interpreted as images of the world and the objects in it. Additionally the brain uses light to physiology (normal functions of living and gene expression) regulate mood, and behavior with these signals from the retina cells.
The eye's anatomy
Some important features.
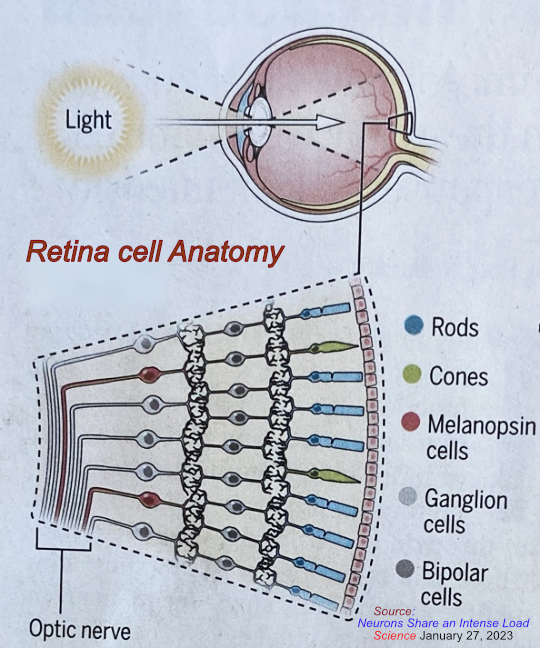
Retina anatomy
Neurons include
- Rods
- Cones
- Melanopsin which sense light with a G protein-coupled receptor. Include less than 1% of the retinal output neorons, however, is important to synchronize the body's biological (circadian) rhythms for sleep, attention, and energy use. They respond over longer periods of time so that together they can signal a larger range of intensity (day and night) than single neurons that create images in real time.
![]()