Cardiovascular system review key:
What is the cardiovascular system?
Includes the heart, blood vessels, and substances they transport through the body. The heart circulates blood 24 hours a day to and from the cells through the arteries, veins, and capillaries. The blood transports gases, nutrients, waste products, white blood cells (leukocytes), hormones, and chemicals as a response to the bodies need.
Describe functions of the cardiovascular system.
- Transfers oxygen from the lungs to the body.
- Transfers carbon dioxide from cells to the lungs where it is exhaled.
- Transfers nutrients from food to organs and cells.
- Transfers solid waste products (salt, nitrogen) to the kidneys for removal.
- Transports white blood cells (leukocytes), hormones, to maintain body health.
Parts and functions
Name things that are in the blood.
Platelets, white blood cells or leukocytes, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hemoglobin, plasma
Match the words in the word bank to the function and label the diagram.
- ___ muscle _________ tissue that makes the heart.
- ___ capillary ________ smallest type of blood vessels in the human body that connect arteries and veins.
- ___ artery __________ type of blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart.
- ___ carbon dioxide _____ blood going to the lungs has more of this than blood leaving it.
- ___ pulse ___________ surge felt in blood vessels.
- ___ white blood cells or leukocyte cells ______ substance in blood that surround and ingest matter that causes infections.
- ___ veins ___________ blood going to the heart from the body travels mostly in these vessels.
- ___ blood pressure _____ is the measure of force on the blood vessel walls.
- ___ an organ _________ the heart is.
- ___ aorta ___________ largest blood vessel in a body.
- ___ platelets _________ stops bleeding and help wounds by forming clots and scabs.
- ___ circulatory or cardiovascular _______ system that transports blood.
- ___ blood type ________ needs to match or a blood transfusion.
- ___ plasma __________ the fluid in which other parts of the blood are suspended.
- ___ oxygen __________ blood leaving the lungs has more of this in it.
- ___ red _____________ the color of blood.
- ___ hemoglobin _______ substance in red blood cells that help transport oxygen and carbon dioxide around the body.
Label parts on the diagram and draw arrows to show the flow of blood.
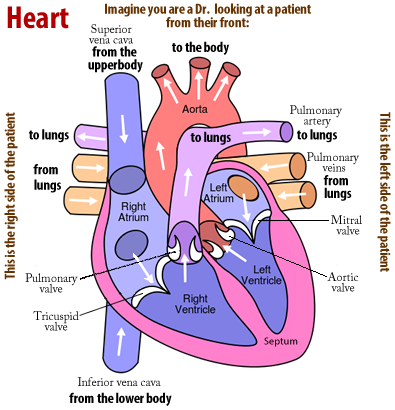
Label arteries and veins
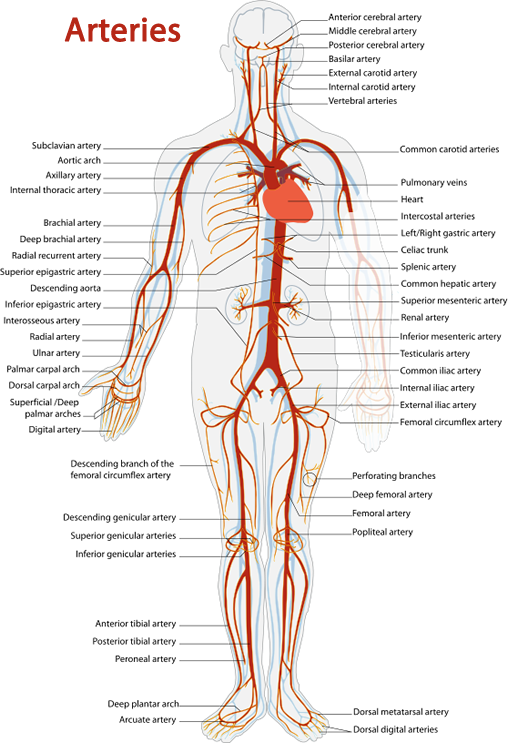
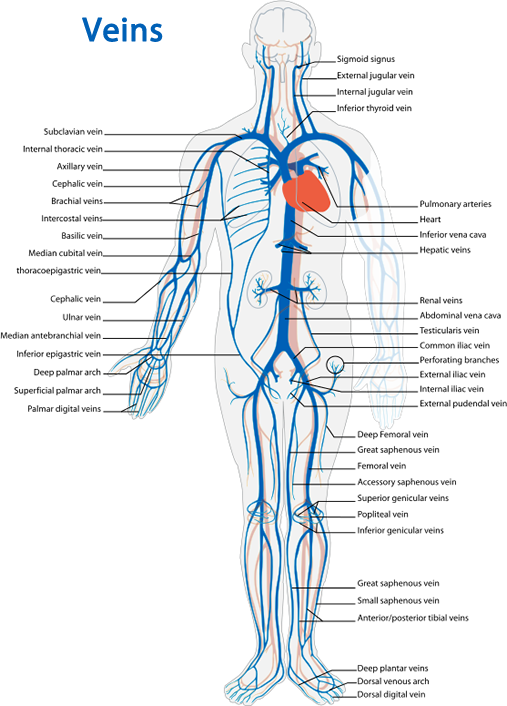
Word bank
red, blue, carbon dioxide, blood type, blood pressure, ventricles, oxygen, aorta, veins, heart, auricles, blood, capillary, artery, hemoglobin, skin, platelets, epidermis, blood vessels, blood cells, leukocyte cells, hemoglobin, plasma, white blood cells, pressure, muscle, vein, pulse, left atrium, right atrium, left ventricle, right ventricle, valve, cardiovascular,
Describe ways to care for the circulatory system.
- Eat a balanced diet
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Check your blood pressure and if it isn't in the normal range have a medical check up
- Participate in aerobic exercise at least three times a week for 50 minutes raising your heart rate so that you are warm and slightly out of breath for one hundred-fifty minutes a week.
- Avoid tobacco products including second hand smoke
- Avoid illegal drug use
- Get regular medical check ups
Describe health related care issues for the circulatory system.
- Anemia is when the blood doesn't carry enough oxygen. May be too few red blood cells, low hemoglobin, or lack of iron. Treatment is usually iron supplements.
- Congenital heart defects are problems present at and before birth. A hole in the heart's septum or a misformed valve. Caused by genetic factors or poor health of the mother during pregnancy. Treatment can be drugs, surgery, and a heart transplant.
- Heart murmur is caused by a hole in the heart or malfunctioning valve. If serious enough, it may require surgery.
- Hemophilia is an inherited disease that causes the blood not to clot. Bruising and uncontrolled bleeding after an injury. Treated with injection of proteins to stimulate clotting.
- Leukemia is a cancer in which there are too many leukocyte cells or they are abnormally formed. This can cause infection, anemia, and bleeding. Treatment is chemotherapy, radiation, and bone marrow transplant.
- Sickle cell is a disease where the gene that makes hemoglobin, makes sickle-shaped red blood cells instead of round, causing pain and organ damage.
- Varicose veins is caused by valves in veins not closing well enough to prevent back flow of blood.